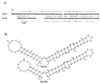
BOXA and BOXB RNAs and their interaction with the ARM of their cognate N proteins. The amino acid-nucleotide interactions are shown to the left except for BOXB of phage 21, for which the structure of the complex is unknown. The sequences of BOXA and BOXA-BOXB spacer are shown to the right. The dots to the left and right of the spacer sequences are for alignment. (A) λ N-ARM-BOXB complex (adapted from reference with permission of the publisher). Open circles, pentagons, and rectangles represent phosphates, riboses, and bases, respectively. Watson-Crick base pairs (||||) are indicated. The zigzag line denotes a sheared G · A base pair. Open circles, open rectangles, and arrowheads depict ionic, hydrophobic, and hydrogen-bonding interactions, respectively. Guanine-11, indicated by a bold rectangle, is extruded from the BOXB loop (see text). (B) P22 N-ARM-BOXB complex (adapted from reference with permission of the publisher). Open circles, pentagons, rectangles, and ovals represent phosphates, riboses, bases, and amino acids, respectively. The solid pentagons indicate riboses with a C2′-
endo pucker. Base stacking (

), intermolecular hydrogen bonding or electrostatic interactions (<-----), intermolecular hydrophobic or van der Waals interactions (←), intramolecular hydrogen bonds (––––) and Watson-Crick base pairs (|||||) are indicated. Cytosine-11 is extruded from the loop (see text). Note that the amino-terminal amino acid residue in the complex corresponds to Asn-14 in the complete protein (Fig. 1), and the displayed amino acids are numbered accordingly. (C) NUTL site of phage 21. The arrows indicate the inverted sequence repeats of BOXB.


 ), intermolecular hydrogen bonding or electrostatic interactions (<-----), intermolecular hydrophobic or van der Waals interactions (←), intramolecular hydrogen bonds (––––) and Watson-Crick base pairs (|||||) are indicated. Cytosine-11 is extruded from the loop (see text). Note that the amino-terminal amino acid residue in the complex corresponds to Asn-14 in the complete protein (Fig. 1), and the displayed amino acids are numbered accordingly. (C) NUTL site of phage 21. The arrows indicate the inverted sequence repeats of BOXB.
), intermolecular hydrogen bonding or electrostatic interactions (<-----), intermolecular hydrophobic or van der Waals interactions (←), intramolecular hydrogen bonds (––––) and Watson-Crick base pairs (|||||) are indicated. Cytosine-11 is extruded from the loop (see text). Note that the amino-terminal amino acid residue in the complex corresponds to Asn-14 in the complete protein (Fig. 1), and the displayed amino acids are numbered accordingly. (C) NUTL site of phage 21. The arrows indicate the inverted sequence repeats of BOXB.