The mithramycin gene cluster of Streptomyces argillaceus contains a positive regulatory gene and two repeated DNA sequences that are located at both ends of the cluster
- PMID: 9882681
- PMCID: PMC93421
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.181.2.642-647.1999
The mithramycin gene cluster of Streptomyces argillaceus contains a positive regulatory gene and two repeated DNA sequences that are located at both ends of the cluster
Abstract
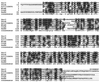
Sequencing of a 4.3-kb DNA region from the chromosome of Streptomyces argillaceus, a mithramycin producer, revealed the presence of two open reading frames (ORFs). The first one (orfA) codes for a protein that resembles several transport proteins. The second one (mtmR) codes for a protein similar to positive regulators involved in antibiotic biosynthesis (DnrI, SnoA, ActII-orf4, CcaR, and RedD) belonging to the Streptomyces antibiotic regulatory protein (SARP) family. Both ORFs are separated by a 1.9-kb, apparently noncoding region. Replacement of the mtmR region by an antibiotic resistance cassette completely abolished mithramycin biosynthesis. Expression of mtmR in a high-copy-number vector in S. argillaceus caused a 16-fold increase in mithramycin production. The mtmR gene restored actinorhodin production in Streptomyces coelicolor JF1 mutant, in which the actinorhodin-specific activator ActII-orf4 is inactive, and also stimulated actinorhodin production by Streptomyces lividans TK21. A 241-bp region located 1.9 kb upstream of mtmR was found to be repeated approximately 50 kb downstream of mtmR at the other end of the mithramycin gene cluster. A model to explain a possible route for the acquisition of the mithramycin gene cluster by S. argillaceus is proposed.
Figures


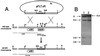


References
-
- Aguirrezabalaga, I. Unpublished data.
-
- Altschul S F, Gish W, Miller W, Myers E W, Lipman D J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Arias, P., M. A. Fernández-Moreno, and F. Malpartida. Personal communication.
-
- Belanger A E, Besra G S, Ford M E, Mikusova K, Belisle J T, Brennan P J, Inamine J M. The embAB genes of Mycobacterium avium encode an arabinosyl transferase involved in cell wall arabinan biosynthesis that is the target for the antimycobacterial drug ethambutol. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:11919–11924. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bibb M J, Cohen S N. Gene expression in Streptomyces: construction and application of promoter-probe plasmid vectors in Streptomyces. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;187:265–277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

