Targeted mutagenesis by duplication insertion in the radioresistant bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans: radiation sensitivities of catalase (katA) and superoxide dismutase (sodA) mutants
- PMID: 9882685
- PMCID: PMC93425
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.181.2.666-669.1999
Targeted mutagenesis by duplication insertion in the radioresistant bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans: radiation sensitivities of catalase (katA) and superoxide dismutase (sodA) mutants
Abstract
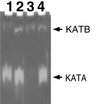
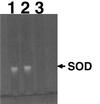
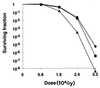
Deinococcus radiodurans R1 is extremely resistant to both oxidative stress and ionizing radiation. A simple and general targeted mutagenesis method was developed to generate catalase (katA) and superoxide dismutase (sodA) mutants. Both mutants were shown to be more sensitive to ionizing radiation than the wild type.
Figures

References
-
- Bauer A W, Kirby W M, Sherris J C, Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Patrol. 1966;45:493–496. - PubMed
-
- Beauchamp C, Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1971;44:276–287. - PubMed
-
- Bradford M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Carbonneau M A, Melin A M, Perromat A, Clerc M. The action of free radicals on Deinococcus radiodurans carotenoids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989;275:244–251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

