A novel leukocyte adhesion deficiency caused by expressed but nonfunctional beta2 integrins Mac-1 and LFA-1
- PMID: 9884339
- PMCID: PMC407855
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI3312
A novel leukocyte adhesion deficiency caused by expressed but nonfunctional beta2 integrins Mac-1 and LFA-1
Abstract
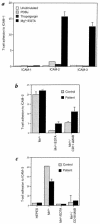
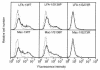
In the leukocyte adhesion deficiency (LAD)-1 syndrome, there is diminished expression of beta2(CD18) integrins. This is caused by lesions in the beta2-subunit gene and gives rise to recurrent bacterial infections, impaired pus formation, and poor wound healing. We describe a patient with clinical features compatible with a moderately severe phenotype of LAD-1 but who expresses the beta2 integrins lymphocyte function- associated molecule (LFA)-1 and Mac-1 at 40%-60% of normal levels. This level of expression should be adequate for normal integrin function, but both the patient's Mac-1 on neutrophils and LFA-1 on T cells failed to bind ligands such as fibrinogen and intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1, respectively, or to display a beta2-integrin activation epitope after adhesion-inducing stimuli. Unexpectedly, divalent cation treatment induced the patient's T cells to bind to ICAM-2 and ICAM-3. Sequencing of the patient's two CD18 alleles revealed the mutations S138P and G273R. Both mutations are in the beta2-subunit conserved domain, with S138P a putative divalent cation coordinating residue in the metal ion-dependent adhesion site (MIDAS) motif. After K562 cell transfection with alpha subunits, the mutated S138P beta subunit was coexpressed but did not support function, whereas the G273R mutant was not expressed. In summary, the patient described here exhibits failure of the beta2 integrins to function despite adequate levels of cell-surface expression.
Figures
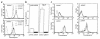

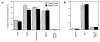

References
-
- Butcher EC, Picker JL. Lymphocyte homing and homeostasis. Science. 1996;272:60–66. - PubMed
-
- Brown EJ. Adhesive interactions in the immune system. Trends Cell Biol. 1997;7:289–295. - PubMed
-
- Bachmann MF, et al. Distinct roles for LFA-1 and CD28 during activation of naive T cells: adhesion versus costimulation. Immunity. 1997;7:549–557. - PubMed
-
- Brown EJ. Complement receptors and phagocytosis. Curr Opin Immunol. 1991;3:76–82. - PubMed
-
- Ross GD, Reed W, Dalzell JG, Becker SE, Hogg N. Macrophage cytoskeleton association with CR3 and CR4 regulates receptor mobility and phagocytosis of iC3b-opsonized erythrocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 1992;51:109–117. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

