Localization of matrix metalloproteinase 9 to the cell surface provides a mechanism for CD44-mediated tumor invasion
- PMID: 9887098
- PMCID: PMC316376
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.13.1.35
Localization of matrix metalloproteinase 9 to the cell surface provides a mechanism for CD44-mediated tumor invasion
Abstract
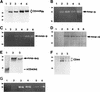
The cell surface hyaluronan receptor CD44 promotes tumor growth and metastasis by mechanisms that remain poorly understood. We show here that CD44 associates with a proteolytic form of the matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) on the surface of mouse mammary carcinoma and human melanoma cells. CD44-associated cell surface MMP-9 promotes cell-mediated collagen IV degradation in vitro and mediates tumor cell invasion of G8 myoblast monolayers. Several distinct CD44 isoforms coprecipitate with MMP-9 and CD44/MMP-9 coclustering is observed to be dependent on the ability of CD44 to form hyaluronan-induced aggregates. Disruption of CD44/MMP-9 cluster formation, by overexpression of soluble or truncated cell surface CD44, is shown to inhibit tumor invasiveness in vivo. Our observations indicate that CD44 serves to anchor MMP-9 on the cell surface and define a mechanism for CD44-mediated tumor invasion.
Figures



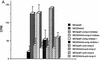
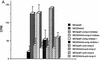
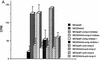
References
-
- Alexander CM, Hansell EJ, Behrendtsen O, Flannery ML, Kishnani NS, Hawkes SP, Werb Z. Expression and function of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors at maternal-embryonic boundary during mouse embryo implantation. Development. 1996;122:1723–1736. - PubMed
-
- Aruffo A, Stamenkovic I, Melnick M, Underhill CB, Seed B. CD44 is the principal cell surface receptor for hyaluronate. Cell. 1990;61:1303–1313. - PubMed
-
- Basbaum C, Werb Z. Focalized proteolysis: Spatial and temporal regulation of extracellular matrix degradation at the cell surface. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996;8:731–738. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
