Clinical evaluation of an in-house reverse transcription-competitive PCR for quantitation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA in plasma
- PMID: 9889213
- PMCID: PMC84299
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.37.2.333-338.1999
Clinical evaluation of an in-house reverse transcription-competitive PCR for quantitation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA in plasma
Abstract
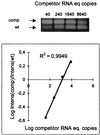
An in-house reverse transcription (RT)-competitive PCR (RT-cPCR) for the quantitation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) RNA in plasma samples was developed and validated. The procedure involves (i) extraction of RNA with spin columns, (ii) ready-to-use bead-mediated RT, (iii) competitive PCR in a microtiter plate, (iv) agarose gel electrophoresis of the reaction products, and (v) densitometric analysis of the digitized image of the gel. Quadruplicate tests and dilution studies showed that the sensitivity and intertest coefficient of variability of the RT-cPCR are comparable to those of the reference AMPLICOR HIV-1 MONITOR test. The results obtained by the two assays with a panel of 45 clinical samples were in good agreement (mean difference, 0.36 +/- 0.25 log units). Analysis of 1,982 clinical samples by the in-house RT-cPCR yielded the typical range of plasma HIV-1 RNA levels with the expected inverse correlation between CD4 counts and HIV-1 RNA titers. In addition, testing of plasma from 36 subjects at weeks 0 and 4 with respect to the time of initiation of protease inhibitor therapy detected a significant decrease in HIV-1 viremia. The mean reduction in the HIV-1 RNA level was 0.914 log unit for those receiving saquinavir (P = 0.0210), 1.584 log units for those receiving indinavir (P = 0.0047), and 1.904 log units for those receiving ritonavir (P < 0.0001). The in-house RT-cPCR assay is simple to develop and perform and allows quantitation of HIV-1 RNA in 100 to 200 samples per operator per week. Since the cost is 1/8 to 1/10 of those of reference commercial assays, this procedure could be conveniently used in medium-scale laboratories.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The effect of high-dose saquinavir on viral load and CD4+ T-cell counts in HIV-infected patients.Ann Intern Med. 1996 Jun 15;124(12):1039-50. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-124-12-199606150-00003. Ann Intern Med. 1996. PMID: 8633817 Clinical Trial.
-
Performance characteristics of the QUANTIPLEX HIV-1 RNA 3.0 assay for detection and quantitation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA in plasma.J Clin Microbiol. 2000 Aug;38(8):2837-45. doi: 10.1128/JCM.38.8.2837-2845.2000. J Clin Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10921936 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the Quantiplex version 3.0 assay and a sensitized Amplicor monitor assay for measurement of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA levels in plasma samples.J Clin Microbiol. 1999 Nov;37(11):3612-4. doi: 10.1128/JCM.37.11.3612-3614.1999. J Clin Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10523562 Free PMC article.
-
Time to HIV-1 RNA suppression below 5 copies/ml during first-line protease inhibitor-based antiretroviral treatment - any impact of residual viremia on treatment success?AIDS Rev. 2013 Oct-Dec;15(4):230-6. AIDS Rev. 2013. PMID: 24322383 Review.
-
Impact of viral load testing on patient care.Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1999 Nov;123(11):1011-4. doi: 10.5858/1999-123-1011-IOVLTO. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1999. PMID: 10539898 Review.
Cited by
-
Sequencing of One Unique Recombinant CRF85_BC/CRF01_AE Genome and Two Partial Genomes from Ningxia, China.Viruses. 2025 Apr 30;17(5):655. doi: 10.3390/v17050655. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40431673 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient methodologies for sensitive HIV-1 RNA quantitation from plasma and vaginal secretions.J Clin Virol. 2009 Dec;46(4):309-13. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2009.08.015. Epub 2009 Sep 23. J Clin Virol. 2009. PMID: 19783472 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma levels of soluble CD27: a simple marker to monitor immune activation during potent antiretroviral therapy in HIV-1-infected subjects.Clin Exp Immunol. 2002 Mar;127(3):486-94. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2002.01786.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11966765 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Bagnarelli P, Menzo S, Valenza A, Paolucci S, Petroni S, Scalise G, Sampaolesi R, Manzin A, Varaldo P E, Clementi M. Quantitative molecular monitoring of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 activity during therapy with specific antiretroviral compounds. J Clin Microbiol. 1995;33:16–23. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bisset L R, Rothen M, Joller-Jemelka H I, Dubs R W, Grob P J, Opravil M. Change in circulating levels of the chemokines macrophage inflammatory proteins 1 alpha and 11 beta, RANTES, monocyte chemotactic protein-1 and interleukin-16 following treatment of severely immunodeficient HIV-infected individuals with indinavir. AIDS. 1997;11:485–491. - PubMed
-
- Clementi M, Menzo S, Bagnarelli P, Manzin A, Valenza A, Varaldo P E. Quantitative PCR and RT-PCR in virology. PCR Methods Appl. 1993;2:191–196. - PubMed
-
- Coste J, Montes B, Reynes J, Peeters M, Segarra C, Vendrell J P, Delaporte E, Segondy M. Comparative evaluation of three assays for the quantitation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA in plasma. J Med Virol. 1996;50:293–302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

