Amino acid signaling in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a permease-like sensor of external amino acids and F-Box protein Grr1p are required for transcriptional induction of the AGP1 gene, which encodes a broad-specificity amino acid permease
- PMID: 9891035
- PMCID: PMC116030
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.2.989
Amino acid signaling in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a permease-like sensor of external amino acids and F-Box protein Grr1p are required for transcriptional induction of the AGP1 gene, which encodes a broad-specificity amino acid permease
Abstract
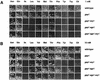
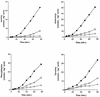
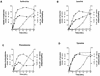
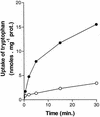
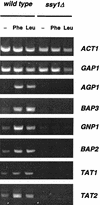
The SSY1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes a member of a large family of amino acid permeases. Compared to the 17 other proteins of this family, however, Ssy1p displays unusual structural features reminiscent of those distinguishing the Snf3p and Rgt2p glucose sensors from the other proteins of the sugar transporter family. We show here that SSY1 is required for transcriptional induction, in response to multiple amino acids, of the AGP1 gene encoding a low-affinity, broad-specificity amino acid permease. Total noninduction of the AGP1 gene in the ssy1Delta mutant is not due to impaired incorporation of inducing amino acids. Conversely, AGP1 is strongly induced by tryptophan in a mutant strain largely deficient in tryptophan uptake, but it remains unexpressed in a mutant that accumulates high levels of tryptophan endogenously. Induction of AGP1 requires Uga35p(Dal81p/DurLp), a transcription factor of the Cys6-Zn2 family previously shown to participate in several nitrogen induction pathways. Induction of AGP1 by amino acids also requires Grr1p, the F-box protein of the SCFGrr1 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex also required for transduction of the glucose signal generated by the Snf3p and Rgt2p glucose sensors. Systematic analysis of amino acid permease genes showed that Ssy1p is involved in transcriptional induction of at least five genes in addition to AGP1. Our results show that the amino acid permease homologue Ssy1p is a sensor of external amino acids, coupling availability of amino acids to transcriptional events. The essential role of Grr1p in this amino acid signaling pathway lends further support to the hypothesis that this protein participates in integrating nutrient availability with the cell cycle.
Figures


References
-
- Alagramam K, Naider F, Becker J M. A recognition component of the ubiquitin system is required for peptide transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Microbiol. 1995;15:225–234. - PubMed
-
- André B. The UGA3 gene regulating the GABA catabolic pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae codes for a putative zinc-finger protein acting on RNA amount. Mol Gen Genet. 1990;220:269–276. - PubMed
-
- André B. An overview of membrane transport proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 1995;11:1575–1611. - PubMed
-
- André B, Hein C, Grenson M, Jauniaux J C. Cloning and expression of the UGA4 gene coding for the inducible GABA-specific transport protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1993;237:17–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
