Selective interaction of vitamin D receptor with transcriptional coactivators by a vitamin D analog
- PMID: 9891040
- PMCID: PMC116035
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.2.1049
Selective interaction of vitamin D receptor with transcriptional coactivators by a vitamin D analog
Abstract
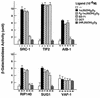
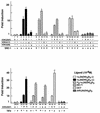
The nuclear vitamin D receptor (VDR) is a member of a nuclear receptor superfamily and acts as a ligand-dependent transcription factor. A family of cotranscriptional activators (SRC-1, TIF2, and AIB-1) interacts with and activates the transactivation function of nuclear receptors in a ligand-dependent way. We examined interaction of VDR with these coactivators that was induced by several vitamin D analogs, since they exert differential subsets of the biological action of vitamin D through unknown mechanisms. Unlike other vitamin D analogs tested, OCT (22-oxa-1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3) induced interaction of VDR with TIF2 but not with SRC-1 or AIB-1. Consistent with these interactions, only TIF2 was able to potentiate the transactivation function of VDR bound to OCT. Thus, the present findings suggest that the structure of VDR is altered in a vitamin D analog-specific way, resulting in selective interactions of VDR with coactivators. Such selective interaction of coactivators with VDR may specify the array of biological actions of a vitamin D analog like OCT, possibly through activating a particular set of target gene promoters.
Figures
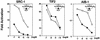
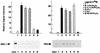

Similar articles
-
Vitamin D analogue-specific recruitment of vitamin D receptor coactivators.J Bone Miner Res. 2002 May;17(5):879-90. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.2002.17.5.879. J Bone Miner Res. 2002. PMID: 12009019
-
Synergistic activation of the prolactin promoter by vitamin D receptor and GHF-1: role of the coactivators, CREB-binding protein and steroid hormone receptor coactivator-1 (SRC-1).Mol Endocrinol. 1999 Jul;13(7):1141-54. doi: 10.1210/mend.13.7.0320. Mol Endocrinol. 1999. PMID: 10406465
-
Nuclear coactivator-62 kDa/Ski-interacting protein is a nuclear matrix-associated coactivator that may couple vitamin D receptor-mediated transcription and RNA splicing.J Biol Chem. 2003 Sep 12;278(37):35325-36. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M305191200. Epub 2003 Jul 2. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12840015
-
Vitamin D receptor and nuclear receptor coactivators: crucial interactions in vitamin D-mediated transcription.Steroids. 2001 Mar-May;66(3-5):171-6. doi: 10.1016/s0039-128x(00)00200-2. Steroids. 2001. PMID: 11179724 Review.
-
The vitamin D hormone and its nuclear receptor: molecular actions and disease states.J Endocrinol. 1997 Sep;154 Suppl:S57-73. J Endocrinol. 1997. PMID: 9379138 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and characterization of noncalcemic, tissue-selective, nonsecosteroidal vitamin D receptor modulators.J Clin Invest. 2006 Apr;116(4):892-904. doi: 10.1172/JCI25901. Epub 2006 Mar 9. J Clin Invest. 2006. PMID: 16528410 Free PMC article.
-
1α,25(OH)2-3-epi-vitamin D3, a natural physiological metabolite of vitamin D3: its synthesis, biological activity and crystal structure with its receptor.PLoS One. 2011 Mar 31;6(3):e18124. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018124. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21483824 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand-selective potentiation of rat mineralocorticoid receptor activation function 1 by a CBP-containing histone acetyltransferase complex.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Jun;22(11):3698-706. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.11.3698-3706.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. Retraction in: Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Mar;34(5):916. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00018-14. PMID: 11997506 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Vitamin D receptor activator selectivity in the treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism: understanding the differences among therapies.Drugs. 2007;67(14):1981-98. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200767140-00002. Drugs. 2007. PMID: 17883283 Review.
-
Drosophila TRAP230/240 are essential coactivators for Atonal in retinal neurogenesis.Dev Biol. 2007 Aug 15;308(2):322-30. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.05.029. Epub 2007 May 26. Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17585897 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abe J, Moriya Y, Saito M, Sugawara Y, Suda T, Nishii Y. Modulation of cell growth, differentiation, and production of interleukin-3 by 1 alpha, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in the murine myelomonocytic leukemia cell line WEHI-3. Cancer Res. 1986;53:2534–2537. - PubMed
-
- Abe J, Nakano T, Nishii Y, Matsumoto T, Ogata E, Ikeda K. A novel vitamin D3 analog, 22-oxa-1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, inhibits the growth of human breast cancer in vitro and in vivo without causing hypercalcemia. Endocrinology. 1991;129:832–837. - PubMed
-
- Anzick S L, Kononen J, Walker R L, Azorsa D O, Tanner M M, Guan X Y, Sauter G, Kallioniemi O P, Trent J M, Meltzer P S. AIB1, a steroid receptor coactivator amplified in breast and ovarian cancer. Science. 1997;277:965–968. - PubMed
-
- Beato M, Herrlich P, Schutz G. Steroid hormone receptors: many actors in search of a plot. Cell. 1995;83:851–857. - PubMed
-
- Bikle D D, Pillai S. Vitamin D, calcium, and epidermal differentiation. Endocr Rev. 1993;14:3–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
