Retinoblastoma protein contains a C-terminal motif that targets it for phosphorylation by cyclin-cdk complexes
- PMID: 9891042
- PMCID: PMC116037
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.2.1068
Retinoblastoma protein contains a C-terminal motif that targets it for phosphorylation by cyclin-cdk complexes
Abstract
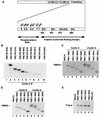
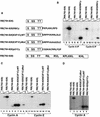
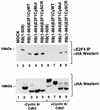
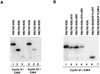
Stable association of certain proteins, such as E2F1 and p21, with cyclin-cdk2 complexes is dependent upon a conserved cyclin-cdk2 binding motif that contains the core sequence ZRXL, where Z and X are usually basic. In vitro phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein, pRB, by cyclin A-cdk2 and cyclin E-cdk2 was inhibited by a short peptide spanning the cyclin-cdk2 binding motif present in E2F1. Examination of the pRB C terminus revealed that it contained sequence elements related to ZRXL. Site-directed mutagenesis of one of these sequences, beginning at residue 870, impaired the phosphorylation of pRB in vitro. A synthetic peptide spanning this sequence also inhibited the phosphorylation of pRB in vitro. pRB C-terminal truncation mutants lacking this sequence were hypophosphorylated in vitro and in vivo despite the presence of intact cyclin-cdk phosphoacceptor sites. Phosphorylation of such mutants was restored by fusion to the ZRXL-like motif derived from pRB or to the ZRXL motifs from E2F1 or p21. Phospho-site-specific antibodies revealed that certain phosphoacceptor sites strictly required a C-terminal ZRXL motif whereas at least one site did not. Furthermore, this residual phosphorylation was sufficient to inactivate pRB in vivo, implying that there are additional mechanisms for directing cyclin-cdk complexes to pRB. Thus, the C terminus of pRB contains a cyclin-cdk interaction motif of the type found in E2F1 and p21 that enables it to be recognized and phosphorylated by cyclin-cdk complexes.
Figures





References
-
- Adams P D, Kaelin W G. Transcriptional control by E2F. Semin Cancer Biol. 1995;6:99–108. - PubMed
-
- Bartkova J, Lukas J, Muller H, Lutzhoft D, Strauss M, Bartek J. Cyclin D1 protein expression and function in human breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 1994;57:353–361. - PubMed
-
- Cantley L C, Auger K R, Carpenter C, Duckworth B, Graziani A, Kapeller R, Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991;64:281–302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
