The MKK7 gene encodes a group of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase kinases
- PMID: 9891090
- PMCID: PMC116085
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.2.1569
The MKK7 gene encodes a group of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase kinases
Abstract
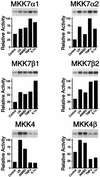
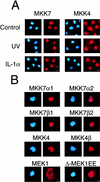
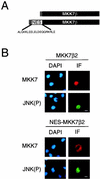
The c-Jun NH2-terminal protein kinase (JNK) is a member of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) group and is an essential component of a signaling cascade that is activated by exposure of cells to environmental stress. JNK activation is regulated by phosphorylation on both Thr and Tyr residues by a dual-specificity MAPK kinase (MAPKK). Two MAPKKs, MKK4 and MKK7, have been identified as JNK activators. Genetic studies demonstrate that MKK4 and MKK7 serve nonredundant functions as activators of JNK in vivo. We report here the molecular cloning of the gene that encodes MKK7 and demonstrate that six isoforms are created by alternative splicing to generate a group of protein kinases with three different NH2 termini (alpha, beta, and gamma isoforms) and two different COOH termini (1 and 2 isoforms). The MKK7alpha isoforms lack an NH2-terminal extension that is present in the other MKK7 isoforms. This NH2-terminal extension binds directly to the MKK7 substrate JNK. Comparison of the activities of the MKK7 isoforms demonstrates that the MKK7alpha isoforms exhibit lower activity, but a higher level of inducible fold activation, than the corresponding MKK7beta and MKK7gamma isoforms. Immunofluorescence analysis demonstrates that these MKK7 isoforms are detected in both cytoplasmic and nuclear compartments of cultured cells. The presence of MKK7 in the nucleus was not, however, required for JNK activation in vivo. These data establish that the MKK4 and MKK7 genes encode a group of protein kinases with different biochemical properties that mediate activation of JNK in response to extracellular stimuli.
Figures









References
-
- Ahn N G, Seger R, Krebs E G. The mitogen-activated protein kinase activator. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992;4:992–999. - PubMed
-
- Anafi M, Kiefer F, Gish G D, Mbamalu G, Iscove N N, Pawson T. SH2/SH3 adaptor proteins can link tyrosine kinases to a Ste20-related protein kinase, HPK1. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:27804–27811. - PubMed
-
- Bagrodia S, Derijard B, Davis R J, Cerione R A. Cdc42 and PAK-mediated signaling leads to Jun kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:27995–27998. - PubMed
-
- Bardwell L, Thorner J. A conserved motif at the amino termini of MEKs might mediate high-affinity interaction with the cognate MAPKs. Trends Biochem Sci. 1996;21:373–374. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Levy R, Hooper S, Wilson R, Paterson H F, Marshall C J. Nuclear export of the stress-activated protein kinase p38 mediated by its substrate MAPKAP kinase-2. Curr Biol. 1998;8:1049–1057. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
