Thymidylate synthase protein and p53 mRNA form an in vivo ribonucleoprotein complex
- PMID: 9891091
- PMCID: PMC116086
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.2.1582
Thymidylate synthase protein and p53 mRNA form an in vivo ribonucleoprotein complex
Abstract
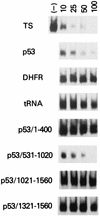
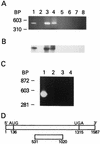
A thymidylate synthase (TS)-ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex composed of TS protein and the mRNA of the tumor suppressor gene p53 was isolated from cultured human colon cancer cells. RNA gel shift assays confirmed a specific interaction between TS protein and the protein-coding region of p53 mRNA, and in vitro translation studies demonstrated that this interaction resulted in the specific repression of p53 mRNA translation. To demonstrate the potential biological role of the TS protein-p53 mRNA interaction, Western immunoblot analysis revealed nearly undetectable levels of p53 protein in TS-overexpressing human colon cancer H630-R10 and rat hepatoma H35(F/F) cell lines compared to the levels in their respective parent H630 and H35 cell lines. Polysome analysis revealed that the p53 mRNA was associated with higher-molecular-weight polysomes in H35 cells compared to H35(F/F) cells. While the level of p53 mRNA expression was identical in parent and TS-overexpressing cell lines, the level of p53 RNA bound to TS in the form of RNP complexes was significantly higher in TS-overexpressing cells. The effect of TS on p53 expression was also investigated with human colon cancer RKO cells by use of a tetracycline-inducible system. Treatment of RKO cells with a tetracycline derivative, doxycycline, resulted in 15-fold-induced expression of TS protein and nearly complete suppression of p53 protein expression. However, p53 mRNA levels were identical in transfected RKO cells in the absence and presence of doxycycline. Taken together, these findings suggest that TS regulates the expression of p53 at the translational level. This study identifies a novel pathway for regulating p53 gene expression and expands current understanding of the potential role of TS as a regulator of cellular gene expression.
Figures



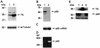



Similar articles
-
Identification of a thymidylate synthase ribonucleoprotein complex in human colon cancer cells.Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):207-13. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.207-213.1994. Mol Cell Biol. 1994. PMID: 8264588 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of a cis-acting regulatory element in the protein coding region of thymidylate synthase mRNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Mar 15;28(6):1381-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.6.1381. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000. PMID: 10684933 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of p53 expression by thymidylate synthase.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Mar 30;96(7):3769-74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.7.3769. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 10097112 Free PMC article.
-
Thymidylate synthase as a translational regulator of cellular gene expression.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002 Jul 18;1587(2-3):174-82. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4439(02)00080-7. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002. PMID: 12084459 Review.
-
The means to an end of tumor cell resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs targeting thymidylate synthase: shoot the messenger.Curr Drug Targets. 2002 Aug;3(4):297-309. doi: 10.2174/1389450023347605. Curr Drug Targets. 2002. PMID: 12102601 Review.
Cited by
-
Topoisomerase I expression is associated with prognosis in postoperative non-small cell lung cancer patients.Thorac Cancer. 2016 Jul;7(4):486-94. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.12359. Epub 2016 May 11. Thorac Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27385993 Free PMC article.
-
Inter-relationship between microsatellite instability, thymidylate synthase expression, and p53 status in colorectal cancer: implications for chemoresistance.BMC Cancer. 2006 Jun 5;6:150. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-6-150. BMC Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16753067 Free PMC article.
-
Antisense-induced down-regulation of thymidylate synthase and enhanced cytotoxicity of 5-FUdR in 5-FUdR-resistant HeLa cells.Br J Pharmacol. 2001 Dec;134(7):1437-46. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704394. Br J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11724749 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of miR-215 in colon cancer.Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2011 Dec;10(4):340-7. doi: 10.1016/j.clcc.2011.06.002. Epub 2011 Jul 12. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21752725 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of a novel thymidylate synthase from deep-sea thermophilic bacteriophage Geobacillus virus E2.Virus Genes. 2008 Oct;37(2):218-24. doi: 10.1007/s11262-008-0258-5. Epub 2008 Jul 22. Virus Genes. 2008. PMID: 18648921
References
-
- Caelles C, Heimberg A, Karin M. p53-dependent apoptosis in the absence of transcriptional activation of p53-target genes. Nature. 1994;370:220–223. - PubMed
-
- Casey J L, Hentze M W, Koeller D M, Caughman S W, Rouault T A, Klausner R D, Harford J B. Iron-responsive elements: regulatory RNA sequences that control mRNA levels and translation. Science. 1988;240:924–928. - PubMed
-
- Chiba I, Takahashi T, Nau M M, D’Amico D, Curiel D T, Mitsudomi T, Buchhagen D L, Carbone D, Piantadosi S, Koga H, Reissman P T, Slamon D J, Holmes E C, Minna J D. Mutations in the p53 gene are frequent in primary, resected non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene. 1990;5:1603–1610. - PubMed
-
- Chomcyznski P, Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987;162:156–159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
