Positive and negative regulation of V(D)J recombination by the E2A proteins
- PMID: 9892611
- PMCID: PMC2192990
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.189.2.289
Positive and negative regulation of V(D)J recombination by the E2A proteins
Abstract
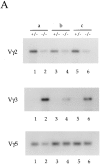
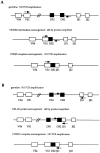
A key feature of B and T lymphocyte development is the generation of antigen receptors through the rearrangement and assembly of the germline variable (V), diversity (D), and joining (J) gene segments. However, the mechanisms responsible for regulating developmentally ordered gene rearrangements are largely unknown. Here we show that the E2A gene products are essential for the proper coordinated temporal regulation of V(D)J rearrangements within the T cell receptor (TCR) gamma and delta loci. Specifically, we show that E2A is required during adult thymocyte development to inhibit rearrangements to the gamma and delta V regions that normally recombine almost exclusively during fetal thymocyte development. The continued rearrangement of the fetal Vgamma3 gene segment in E2A-deficient adult thymocytes correlates with increased levels of Vgamma3 germline transcripts and increased levels of double-stranded DNA breaks at the recombination signal sequence bordering Vgamma3. Additionally, rearrangements to a number of Vgamma and Vdelta gene segments used predominantly during adult development are significantly reduced in E2A-deficient thymocytes. Interestingly, at distinct stages of T lineage development, both the increased and decreased rearrangement of particular Vdelta gene segments is highly sensitive to the dosage of the E2A gene products, suggesting that the concentration of the E2A proteins is rate limiting for the recombination reaction involving these Vdelta regions.
Figures


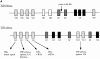
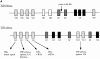






References
-
- Tonegawa S. Somatic generation of antibody diversity. Nature. 1983;302:575–581. - PubMed
-
- Schatz D, Oettinger M, Schlissel M. V(D)J recombination: molecular biology and regulation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:359–383. - PubMed
-
- Oettinger M, Schatz D, Gorka C, Baltimore D. RAG-1 and RAG-2, adjacent genes that synergistically activate V(D)J recombination. Science. 1990;248:1517–1523. - PubMed
-
- McBlane J, van Gent D, Ramsden D, Romeo C, Cuomo C, Gellert M, Oettinger M. Cleavage at a V(D)J recombination signal requires only RAG1 and RAG2 proteins and occurs in two steps. Cell. 1995;83:387–395. - PubMed
-
- Mombaerts P, Iacomini J, Johnson RS, Herrup K, Tonegawa S, Papaioannou VE. RAG-1-deficient mice have no mature B and T lymphocytes. Cell. 1992;68:869–877. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

