Mitochondrial release of caspase-2 and -9 during the apoptotic process
- PMID: 9892620
- PMCID: PMC2192979
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.189.2.381
Mitochondrial release of caspase-2 and -9 during the apoptotic process
Abstract
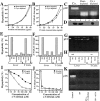
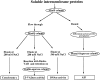
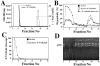
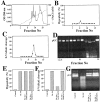
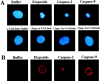
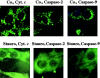
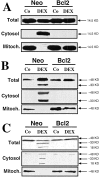
The barrier function of mitochondrial membranes is perturbed early during the apoptotic process. Here we show that the mitochondria contain a caspase-like enzymatic activity cleaving the caspase substrate Z-VAD.afc, in addition to three biological activities previously suggested to participate in the apoptotic process: (a) cytochrome c; (b) an apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) which causes isolated nuclei to undergo apoptosis in vitro; and (c) a DNAse activity. All of these factors, which are biochemically distinct, are released upon opening of the permeability transition (PT) pore in a coordinate, Bcl-2-inhibitable fashion. Caspase inhibitors fully neutralize the Z-VAD.afc-cleaving activity, have a limited effect on the AIF activity, and have no effect at all on the DNase activities. Purification of proteins reacting with the biotinylated caspase substrate Z-VAD, immunodetection, and immunodepletion experiments reveal the presence of procaspase-2 and -9 in mitochondria. Upon induction of PT pore opening, these procaspases are released from purified mitochondria and become activated. Similarly, upon induction of apoptosis, both procaspases redistribute from the mitochondrion to the cytosol and are processed to generate enzymatically active caspases. This redistribution is inhibited by Bcl-2. Recombinant caspase-2 and -9 suffice to provoke full-blown apoptosis upon microinjection into cells. Altogether, these data suggest that caspase-2 and -9 zymogens are essentially localized in mitochondria and that the disruption of the outer mitochondrial membrane occurring early during apoptosis may be critical for their subcellular redistribution and activation.
Figures


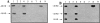
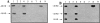
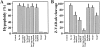
Similar articles
-
Bax-induced caspase activation and apoptosis via cytochrome c release from mitochondria is inhibitable by Bcl-xL.J Biol Chem. 1999 Jan 22;274(4):2225-33. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.4.2225. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 9890985
-
Molecular characterization of mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing factor.Nature. 1999 Feb 4;397(6718):441-6. doi: 10.1038/17135. Nature. 1999. PMID: 9989411
-
Mitochondrio-nuclear translocation of AIF in apoptosis and necrosis.FASEB J. 2000 Apr;14(5):729-39. FASEB J. 2000. PMID: 10744629
-
Mitochondria, the killer organelles and their weapons.J Cell Physiol. 2002 Aug;192(2):131-7. doi: 10.1002/jcp.10111. J Cell Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12115719 Review.
-
Apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF): a novel caspase-independent death effector released from mitochondria.Biochimie. 2002 Feb-Mar;84(2-3):215-22. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(02)01374-3. Biochimie. 2002. PMID: 12022952 Review.
Cited by
-
A 2-methoxyestradiol bis-sulphamoylated derivative induces apoptosis in breast cell lines.Cell Biosci. 2015 Apr 22;5:19. doi: 10.1186/s13578-015-0010-5. eCollection 2015. Cell Biosci. 2015. PMID: 25908963 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuated Leishmanial sphingolipid induces apoptosis in A375 human melanoma cell via both caspase-dependent and -independent pathways.Mol Cell Biochem. 2007 Oct;304(1-2):143-54. doi: 10.1007/s11010-007-9495-5. Epub 2007 May 25. Mol Cell Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17530191
-
The Amaryllidaceae isocarbostyril narciclasine induces apoptosis by activation of the death receptor and/or mitochondrial pathways in cancer cells but not in normal fibroblasts.Neoplasia. 2007 Sep;9(9):766-76. doi: 10.1593/neo.07535. Neoplasia. 2007. PMID: 17898872 Free PMC article.
-
PAX2 suppresses apoptosis in renal collecting duct cells.Am J Pathol. 2000 Sep;157(3):833-42. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64597-X. Am J Pathol. 2000. PMID: 10980123 Free PMC article.
-
Aspirin-induced mucosal cell death in human gastric cells: evidence supporting an apoptotic mechanism.Dig Dis Sci. 2004 Sep;49(9):1518-25. doi: 10.1023/b:ddas.0000042258.41480.30. Dig Dis Sci. 2004. PMID: 15481331
References
-
- Thompson CB. Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science. 1995;267:1456–1462. - PubMed
-
- Kroemer G, Petit PX, Zamzami N, Vayssière J-L, Mignotte B. The biochemistry of apoptosis. FASEB J. 1995;9:1277–1287. - PubMed
-
- Jacobson MD, Weil M, Raff MC. Programmed cell death in animal development. Cell. 1997;88:347–354. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

