Lymphotoxin alpha/beta and tumor necrosis factor are required for stromal cell expression of homing chemokines in B and T cell areas of the spleen
- PMID: 9892622
- PMCID: PMC2192983
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.189.2.403
Lymphotoxin alpha/beta and tumor necrosis factor are required for stromal cell expression of homing chemokines in B and T cell areas of the spleen
Abstract
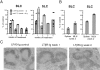
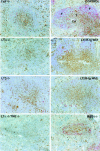
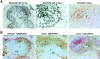
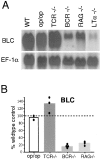
Mice deficient in the cytokines tumor necrosis factor (TNF) or lymphotoxin (LT) alpha/beta lack polarized B cell follicles in the spleen. Deficiency in CXC chemokine receptor 5 (CXCR5), a receptor for B lymphocyte chemoattractant (BLC), also causes loss of splenic follicles. Here we report that BLC expression by follicular stromal cells is defective in TNF-, TNF receptor 1 (TNFR1)-, LTalpha- and LTbeta-deficient mice. Treatment of adult mice with antagonists of LTalpha1beta2 also leads to decreased BLC expression. These findings indicate that LTalpha1beta2 and TNF have a role upstream of BLC/CXCR5 in the process of follicle formation. In addition to disrupted follicles, LT-deficient animals have disorganized T zones. Expression of the T cell attractant, secondary lymphoid tissue chemokine (SLC), by T zone stromal cells is found to be markedly depressed in LTalpha-, and LTbeta-deficient mice. Expression of the SLC-related chemokine, Epstein Barr virus-induced molecule 1 ligand chemokine (ELC), is also reduced. Exploring the basis for the reduced SLC expression led to identification of further disruptions in T zone stromal cells. Together these findings indicate that LTalpha1beta2 and TNF are required for the development and function of B and T zone stromal cells that make chemokines necessary for lymphocyte compartmentalization in the spleen.
Figures

References
-
- Matsumoto M, Fu YX, Molina H, Chaplin DD. Lymphotoxin-alpha-deficient and TNF receptor-I- deficient mice define developmental and functional characteristics of germinal centers. Immunol Rev. 1997;156:137–144. - PubMed
-
- Futterer A, Mink K, Luz A, Kosco-Vilbois MH, Pfeffer K. The lymphotoxin β receptor controls organogenesis and affinity maturation in peripheral lymphoid tissues. Immunity. 1998;9:59–70. - PubMed
-
- Pasparakis M, Alexopoulou L, Episkopou V, Kollias G. Immune and inflammatory responses in TNF alpha–deficient mice: a critical requirement for TNF alpha in the formation of primary B cell follicles, follicular dendritic cell networks and germinal centers, and in the maturation of the humoral immune response. J Exp Med. 1996;184:1397–1411. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Neumann B, Machleidt T, Lifka A, Pfeffer K, Vestweber D, Mak TW, Holzmann B, Kronke M. Crucial role of 55-kilodalton TNF receptor in TNF-induced adhesion molecule expression and leukocyte organ infiltration. J Immunol. 1996;156:1587–1593. - PubMed
-
- Forster R, Mattis AE, Kremmer E, Wolf E, Brem G, Lipp M. A putative chemokine receptor, BLR1, directs B cell migration to defined lymphoid organs and specific anatomic compartments of the spleen. Cell. 1996;87:1–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

