Substrate recognition by class I lysyl-tRNA synthetases: a molecular basis for gene displacement
- PMID: 9892648
- PMCID: PMC15151
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.2.418
Substrate recognition by class I lysyl-tRNA synthetases: a molecular basis for gene displacement
Abstract
Lysyl-tRNA synthetases (LysRSs) are unique amongst the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases in being composed of unrelated class I and class II enzymes. To allow direct comparison between the two types of LysRS, substrate recognition by class I LysRSs was examined. Genes encoding both an archaeal and a bacterial class I enzyme were able to rescue an Escherichia coli strain deficient in LysRS, indicating their ability to functionally substitute for a class II LysRS in vivo. In vitro characterization showed lysine activation and recognition to be tRNA-dependent, an attribute of several class I, but not class II, aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. Examination of tRNA recognition showed that class I LysRSs recognize the same elements in tRNALys as their class II counterparts, namely the discriminator base (N73) and the anticodon. This sequence-specific recognition of the same nucleotides in tRNALys by the two unrelated types of enzyme suggests that tRNALys predates at least one of the LysRSs in the evolution of the translational apparatus. The only observed variation in recognition was that the G2.U71 wobble pair of spirochete tRNALys acts as antideterminant for class II LysRS but does not alter class I enzyme recognition. This difference in tRNA recognition strongly favors the use of a class I-type enzyme to aminoacylate particular tRNALys species and provides a molecular basis for the observed displacement of class II by class I LysRSs in certain bacteria.
Figures


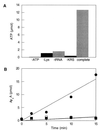
Comment in
-
Genetic code origins: experiments confirm phylogenetic predictions and may explain a puzzle.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Jan 19;96(2):327-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.2.327. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 9892630 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Context-dependent anticodon recognition by class I lysyl-tRNA synthetases.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Dec 19;97(26):14224-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.26.14224. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 11121028 Free PMC article.
-
Functional annotation of class I lysyl-tRNA synthetase phylogeny indicates a limited role for gene transfer.J Bacteriol. 2002 Aug;184(16):4594-600. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.16.4594-4600.2002. J Bacteriol. 2002. PMID: 12142429 Free PMC article.
-
A euryarchaeal lysyl-tRNA synthetase: resemblance to class I synthetases.Science. 1997 Nov 7;278(5340):1119-22. doi: 10.1126/science.278.5340.1119. Science. 1997. PMID: 9353192
-
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthesis: a postgenomic perspective.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2001;66:175-83. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2001.66.175. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2001. PMID: 12762020 Review. No abstract available.
-
The role of the anticodon in recognition of tRNA by aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases.Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1985;32:237-66. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60350-5. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1985. PMID: 3911276 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetases in the Bacterial World.EcoSal Plus. 2016 May;7(1):10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0002-2016. doi: 10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0002-2016. EcoSal Plus. 2016. PMID: 27223819 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rational Design of Aptamer-Tagged tRNAs.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 21;21(20):7793. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207793. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33096801 Free PMC article.
-
Protein synthesis in Escherichia coli with mischarged tRNA.J Bacteriol. 2003 Jun;185(12):3524-6. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.12.3524-3526.2003. J Bacteriol. 2003. PMID: 12775689 Free PMC article.
-
Architecture of Pseudomonas aeruginosa glutamyl-tRNA synthetase defines a subfamily of dimeric class Ib aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 May 13;122(19):e2504757122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2504757122. Epub 2025 May 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40343997
-
Anticodon recognition and discrimination by the alpha-helix cage domain of class I lysyl-tRNA synthetase.Biochemistry. 2007 Oct 2;46(39):11033-8. doi: 10.1021/bi700815a. Epub 2007 Aug 31. Biochemistry. 2007. PMID: 17760422 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gesteland R F, Atkins J F. The RNA World. Plainview, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Lab. Press; 1993.
-
- Schimmel P, Ribas de Pouplana L. Cell. 1995;81:983–986. - PubMed
-
- Shiba K, Motegi H, Schimmel P. Trends Biochem Sci. 1997;22:453–457. - PubMed
-
- Ibba M, Curnow A W, Söll D. Trends Biochem Sci. 1997;22:39–42. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

