Nystagmus in periventricular leucomalacia
- PMID: 9893593
- PMCID: PMC1722754
- DOI: 10.1136/bjo.82.9.1026
Nystagmus in periventricular leucomalacia
Abstract
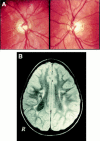
Background/aims: Periventricular leucomalacia (PVL) is a lesion in the immature brain involving the optic radiation. Children with PVL have visual problems including crowding, visual field defects, strabismus, and visual perceptual/cognitive deficits, together with nystagmus. They often have optic nerve hypoplasia seen either as small discs or as large cupping of normal sized optic discs. This study aimed to perform eye movement recordings in a group of children with PVL in order to characterise and classify the nystagmus.
Methods: 19 children with PVL on cerebral imaging underwent eye movement recordings with the Ober-2 infrared reflection technique.
Results: 16 of the 19 subjects had horizontal nystagmus.
Conclusion: The present study shows that nystagmus is commonly seen in children with PVL.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
