Receptor-dependent immune responses in pigs after oral immunization with F4 fimbriae
- PMID: 9916054
- PMCID: PMC96350
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.67.2.520-526.1999
Receptor-dependent immune responses in pigs after oral immunization with F4 fimbriae
Abstract
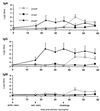
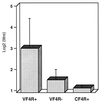
F4 receptor-positive (F4R+) and F4 receptor-negative (F4R-) pigs were orally vaccinated with purified F4 fimbriae of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC). Serum immunoglobulin G (IgG) and IgA responses were readily detected in F4R+ animals, whereas immune responses were not detected in F4R- animals. Even after a subsequent oral infection with virulent F4(+) ETEC and a booster immunization with F4, the F4R- animals remained F4 seronegative whereas the unvaccinated F4R+ pigs exhibited clear IgA and IgG responses. These results clearly demonstrate that F4Rs are a prerequisite for an immune response following oral immunization. Furthermore, indications that oral F4 vaccination can induce mucosal protection were obtained, since the experimental ETEC infection did not induce a systemic booster response or fecal ETEC excretion in orally vaccinated F4R+ pigs, in contrast to the clear immune response and ETEC excretion of unvaccinated F4R+ animals. F4-specific IgA antibodies could be found in the feces of the vaccinated F4R+ pigs. They are secreted at the intestinal mucosal surface and appear to prevent ETEC infection. The F4R-dependent induction of a mucosal immune response can be used as a model to better understand mucosal immunization and mucosal immune responses and can contribute to the development of oral vaccines in veterinary as well as in human medicine.
Figures
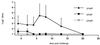
Similar articles
-
F4 receptor-independent priming of the systemic immune system of pigs by low oral doses of F4 fimbriae.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2002 Mar;85(3-4):171-8. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2427(01)00429-9. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2002. PMID: 11943318
-
Induction of immune responses in pigs following oral administration of purified F4 fimbriae.Vaccine. 1999 Apr 9;17(15-16):2020-9. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(98)00406-x. Vaccine. 1999. PMID: 10217602
-
Oral immunisation of pigs with fimbrial antigens of enterotoxigenic E. coli: an interesting model to study mucosal immune mechanisms.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2002 Sep 10;87(3-4):287-90. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2427(02)00054-5. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2002. PMID: 12072248
-
The F4 fimbrial antigen of Escherichia coli and its receptors.Vet Microbiol. 2000 Feb;71(3-4):223-44. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1135(99)00174-1. Vet Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10703706 Review.
-
Adhesion of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in humans and animals.Ciba Found Symp. 1981;80:142-60. doi: 10.1002/9780470720639.ch10. Ciba Found Symp. 1981. PMID: 6114818 Review.
Cited by
-
Production of a subunit vaccine candidate against porcine post-weaning diarrhea in high-biomass transplastomic tobacco.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e42405. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042405. Epub 2012 Aug 3. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22879967 Free PMC article.
-
Role of antigen specific T and B cells in systemic and mucosal immune responses in ETEC and Shigella infections, and their potential to serve as correlates of protection in vaccine development.Vaccine. 2019 Aug 7;37(34):4787-4793. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.03.040. Epub 2019 Jun 20. Vaccine. 2019. PMID: 31230883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fimbrial subunit protein FaeG expressed in transgenic tobacco inhibits the binding of F4ac enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli to porcine enterocytes.Transgenic Res. 2004 Jun;13(3):295-8. doi: 10.1023/b:trag.0000034621.55404.70. Transgenic Res. 2004. PMID: 15359606
-
Saccharomyces cerevisiae modulates immune gene expressions and inhibits ETEC-mediated ERK1/2 and p38 signaling pathways in intestinal epithelial cells.PLoS One. 2011 Apr 4;6(4):e18573. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018573. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21483702 Free PMC article.
-
Swine enteric colibacillosis: Current treatment avenues and future directions.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Oct 28;9:981207. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.981207. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 36387374 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arnouts S. Ph.D. thesis. Leuven, Belgium: Catholic University Leuven; 1994. Somatostatin immunoneutralization in the chicken: immunogen development and effect on growth; p. 42.
-
- Bakker D, Willemsen P T, Simons L H, van Zijderveld F G, de Graaf F K. Characterization of the antigenic and adhesive properties of FaeG, the major subunit of K88 fimbriae. Mol Microbiol. 1992;6:247–255. - PubMed
-
- Clements J D, Hartzog N M, Lyon F L. Adjuvant activity of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin and effect on the induction of oral tolerance in mice to unrelated protein antigens. Vaccine. 1988;6:269–277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

