Involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in interleukin-8 production by human monocytes and polymorphonuclear cells stimulated with lipopolysaccharide or Mycoplasma fermentans membrane lipoproteins
- PMID: 9916078
- PMCID: PMC96374
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.67.2.688-693.1999
Involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in interleukin-8 production by human monocytes and polymorphonuclear cells stimulated with lipopolysaccharide or Mycoplasma fermentans membrane lipoproteins
Abstract
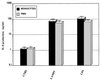
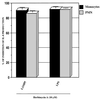
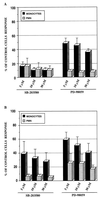
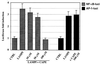
Interleukin-8 (IL-8) is a chemokine that belongs to the alpha-chemokine or CXC subfamily and is produced by a wide variety of human cells, including monocytes and polymorphonuclear cells (PMN). IL-8 is secreted in response to inflammatory stimuli, notably bacterial products such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS), but little is known about the mechanisms by which these agents mediate IL-8 induction. In this report, we show that Mycoplasma fermentans lipid-associated membrane proteins (LAMPf) induce the production of high levels of IL-8 by THP-1 (human monocyte) cells and PMN at the same extent as LPS. It was previously demonstrated that stimulation of monocytic cells with either LPS or LAMPf led to a series of common downstream signaling events, including the activation of protein tyrosine kinase and of mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades. By using PD-98059 and SB203580, two potent and selective inhibitors of MEK1 (a kinase upstream of ERK1/2) and p38, respectively, we have demonstrated that both ERK1/2 and p38 cascades play a key role in the production of IL-8 by monocytes and PMN stimulated with bacterial fractions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways by Mycoplasma fermentans membrane lipoproteins in murine macrophages: involvement in cytokine synthesis.J Immunol. 1998 Feb 1;160(3):1330-9. J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9570551
-
Signal transduction pathways involved in the activation of NF-kappa B, AP-1, and c-fos by Mycoplasma fermentans membrane lipoproteins in macrophages.J Immunol. 1999 Feb 15;162(4):2193-203. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 9973495
-
A Mycoplasma fermentans-derived synthetic lipopeptide induces AP-1 and NF-kappaB activity and cytokine secretion in macrophages via the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways.J Biol Chem. 1998 Dec 18;273(51):34391-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.51.34391. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9852105
-
Suppression of IL-8 gene expression by radicicol is mediated through the inhibition of ERK1/2 and p38 signaling and negative regulation of NF-kappaB and AP-1.Int Immunopharmacol. 2001 Sep;1(9-10):1877-87. doi: 10.1016/s1567-5769(01)00113-8. Int Immunopharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11562079
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinases and nuclear factor-kappaB regulate Helicobacter pylori-mediated interleukin-8 release from macrophages.Biochem J. 2002 Nov 15;368(Pt 1):121-9. doi: 10.1042/BJ20020555. Biochem J. 2002. PMID: 12150710 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Mycoplasma fermentans inhibits the activity of cellular DNA topoisomerase I by activation of PARP1 and alters the efficacy of its anti-cancer inhibitor.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 27;8(8):e72377. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072377. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24013388 Free PMC article.
-
Kruppel-like factor 5 is an important mediator for lipopolysaccharide-induced proinflammatory response in intestinal epithelial cells.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Feb 25;34(4):1216-23. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl014. Print 2006. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16500892 Free PMC article.
-
C1q-bearing immune complexes induce IL-8 secretion in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) through protein tyrosine kinase- and mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent mechanisms: evidence that the 126 kD phagocytic C1q receptor mediates immune complex activation of HUVEC.Clin Exp Immunol. 2001 Sep;125(3):360-7. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2001.01597.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11531942 Free PMC article.
-
Shigella flexneri Interactions with the Basolateral Membrane Domain of Polarized Model Intestinal Epithelium: Role of Lipopolysaccharide in Cell Invasion and in Activation of the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase ERK.Infect Immun. 2002 Mar;70(3):1150-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.3.1150-1158.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 11854195 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-8 is differentially expressed by human-derived monocytic cell line U937 infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv and Mycobacterium marinum.Infect Immun. 2003 Oct;71(10):5480-7. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.10.5480-5487.2003. Infect Immun. 2003. PMID: 14500465 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alessi D R, Cuenda A, Cohen P, Dudley D T, Saltiel A R. PD-98059 is a specific inhibitor of the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:27489–27494. - PubMed
-
- Baggiolini M, Dewald B, Moser B. Interleukin-8 and related chemotactic cytokines—CXC and CC chemokines. Adv Immunol. 1994;55:97–179. - PubMed
-
- Baldari C T, Milia E, Di Somma M M, Baldoni F, Valitutti S, Telford J L. Distinct signaling properties identify functionally different CD4 epitopes. Eur J Immunol. 1995;25:1843–1850. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Baruch A, Michiel D F, Oppenheim J J. Signals and receptors involved in recruitment of inflammatory cells. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:11703–11706. - PubMed
-
- Brasier A R. Reporter system using firefly luciferase. In: Ausubel F M, Brent R, Kingston R E, Moore D D, Seidman J G, Smith J A, Struhl K, editors. Current protocols in molecular biology. New York, N.Y: Green Publishing and John Wiley & Sons; 1994. pp. 9.6.1–9.6.14.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

