Effectiveness of a vaccine composed of heat-killed Candida albicans and a novel mucosal adjuvant, LT(R192G), against systemic candidiasis
- PMID: 9916097
- PMCID: PMC96393
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.67.2.826-833.1999
Effectiveness of a vaccine composed of heat-killed Candida albicans and a novel mucosal adjuvant, LT(R192G), against systemic candidiasis
Abstract
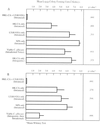
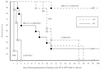
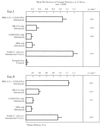
The incidence of fungal infections caused by the opportunistic yeast Candida albicans has increased significantly in recent years. The ability to vaccinate selected patients against the organism would be advantageous. In this paper we describe a potential anti-C. albicans vaccine consisting of heat-killed C. albicans (HK-CA) in combination with the novel mucosal adjuvant LT(R192G), a genetically detoxified form of the heat-labile toxin of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Groups of male CBA/J mice were immunized intranasally on three occasions at weekly intervals with 2 x 10(7) HK-CA per dose, alone or in conjunction with 10 micrograms of LT(R192G) per dose. Two weeks following the last application of antigen, some animals were challenged intravenously (i.v.) with 10(4), 10(5), or 10(6) viable C. albicans to assess protection as measured by survival and/or culture. Some groups of animals were footpad tested with C. albicans mannan to assess delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH), and all the animals were bled for antibody assays. In two independent studies, all the animals immunized with HK-CA plus LT(R192G) were able to eradicate 10(4) C. albicans completely, as determined by kidney culture 4 weeks after challenge. Animals immunized with HK-CA only had reduced levels of C. albicans compared to the adjuvant or saline-only control. Greatly enhanced survival was observed when mice immunized with HK-CA plus LT(R192G) were challenged with 10(5) live C. albicans as well. Animals immunized with HK-CA plus LT(R192G) developed a significant DH response, while those given HK-CA alone developed only marginal DH responses. High immunoglobulin G (IgG) levels to cytoplasmic antigens developed in mice immunized with HK-CA plus LT(R192G), but they were found only after i.v. challenge. Addition of adjuvant shifted the antibody isotype production in i.v.-challenged animals to a response dominated by IgG2a. Clearly, intranasal immunization with killed C. albicans in conjunction with LT(R192G) afforded significant levels of protection. This novel approach offers new possibilities for the development of an effective vaccine against candidiasis for use in humans.
Figures
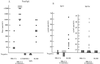

Similar articles
-
Partial protection against experimental vaginal candidiasis after mucosal vaccination with heat-killed Candida albicans and the mucosal adjuvant LT(R192G).Med Mycol. 2002 Jun;40(3):291-9. doi: 10.1080/mmy.40.3.291.299. Med Mycol. 2002. PMID: 12146759
-
Evaluation of the reactogenicity, adjuvanticity and antigenicity of LT(R192G) and LT(R192G/L211A) by intradermal immunization in mice.PLoS One. 2019 Nov 4;14(11):e0224073. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0224073. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31682624 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of intranasal immunization with HIV-gp160 and an HIV-1 env CTL epitope peptide (E7) in combination with the mucosal adjuvant LT(R192G).Vaccine. 2000 Mar 17;18(18):1944-51. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(99)00447-8. Vaccine. 2000. PMID: 10699345
-
New approaches to mucosal immunization.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1999;473:319-37. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-4143-1_34. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1999. PMID: 10659373 Review.
-
A proposal for safety standards for human use of cholera toxin (or Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin) derivatives as an adjuvant of nasal inactivated influenza vaccine.Jpn J Infect Dis. 2000 Jun;53(3):98-106. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2000. PMID: 10957706 Review.
Cited by
-
Vaccines against candidiasis: Status, challenges and emerging opportunity.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Aug 18;12:1002406. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1002406. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36061876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vaccination with recombinant N-terminal domain of Als1p improves survival during murine disseminated candidiasis by enhancing cell-mediated, not humoral, immunity.Infect Immun. 2005 Feb;73(2):999-1005. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.2.999-1005.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 15664943 Free PMC article.
-
Advancing Vaccine Strategies against Candida Infections: Exploring New Frontiers.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Oct 29;11(11):1658. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11111658. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38005990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human papillomavirus virus-like particles are efficient oral immunogens when coadministered with Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin mutant R192G or CpG DNA.J Virol. 2001 May;75(10):4752-60. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.10.4752-4760.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11312347 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccinating against Helicobacter pylori in the developing world.Gut Microbes. 2013 Nov-Dec;4(6):568-76. doi: 10.4161/gmic.27093. Epub 2013 Nov 6. Gut Microbes. 2013. PMID: 24253617 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Balish E, Jensen J, Warner T, Brekke J, Leonard B. Mucosal and disseminated candidiasis in gnotobiotic SCID mice. J Med Vet Mycol. 1993;31:143–154. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee U, Mohapatra L N, Kumar R. Effect of immunization with formalin killed cells in complete Freund’s adjuvant in experimental candidosis. Indian J Med Res. 1985;81:454–458. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

