Roles of PilC and PilE proteins in pilus-mediated adherence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis to human erythrocytes and endothelial and epithelial cells
- PMID: 9916098
- PMCID: PMC96394
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.67.2.834-843.1999
Roles of PilC and PilE proteins in pilus-mediated adherence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis to human erythrocytes and endothelial and epithelial cells
Abstract
Unlike other type 4 pili, the neisserial pili consist of at least two distinct proteins, the highly variable major subunit PilE forming the pilus fiber and the tip-associated adhesin PilC. PilC protein purified either from gonococci or from Escherichia coli interacted with different human epithelial cell lines, primary epithelial and endothelial cells. The binding of PilC protein efficiently prevented the attachment of piliated Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis to these cell types. Fluorescent beads coated with pili prepared from piliated wild-type N. gonorrhoeae also adhered to these cells, in contrast to beads coated with pili prepared from a piliated PilC-deficient mutant. In the latter case, the binding of fluorescent beads was restored after pretreatment of the pilus-loaded beads with purified PilC. Piliated wild-type N. gonorrhoeae, the piliated PilC-deficient mutant, and N. gonorrhoeae pili assembled in Pseudomonas aeruginosa agglutinated human erythrocytes, while nonpiliated gonococci did not. Consistently, purified PilC did not agglutinate or bind to human erythrocytes, suggesting that N. gonorrhoeae PilE is responsible for pilus-mediated hemagglutination.
Figures

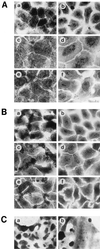
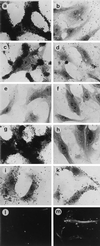
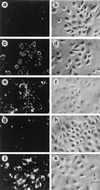
Similar articles
-
PilC of Neisseria meningitidis is involved in class II pilus formation and restores pilus assembly, natural transformation competence and adherence to epithelial cells in PilC-deficient gonococci.Mol Microbiol. 1997 Mar;23(5):879-92. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1997.2631630.x. Mol Microbiol. 1997. PMID: 9076726
-
Neisseria PilC protein identified as type-4 pilus tip-located adhesin.Nature. 1995 Jan 26;373(6512):357-9. doi: 10.1038/373357a0. Nature. 1995. PMID: 7830772
-
CD46-independent binding of neisserial type IV pili and the major pilus adhesin, PilC, to human epithelial cells.Infect Immun. 2005 May;73(5):3072-82. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.5.3072-3082.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 15845515 Free PMC article.
-
Chaperone-assisted assembly and molecular architecture of adhesive pili.Annu Rev Microbiol. 1991;45:383-415. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.45.100191.002123. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1991. PMID: 1683764 Review.
-
Transformation competence and type-4 pilus biogenesis in Neisseria gonorrhoeae--a review.Gene. 1997 Jun 11;192(1):125-34. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(97)00038-3. Gene. 1997. PMID: 9224882 Review.
Cited by
-
Type IV pilin proteins: versatile molecular modules.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2012 Dec;76(4):740-72. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00035-12. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2012. PMID: 23204365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alanine 32 in PilA is important for PilA stability and type IV pili function in Myxococcus xanthus.Microbiology (Reading). 2011 Jul;157(Pt 7):1920-1928. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.049684-0. Epub 2011 Apr 14. Microbiology (Reading). 2011. PMID: 21493683 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation of the conserved calcium-binding motif in Neisseria gonorrhoeae PilC1 impacts adhesion but not piliation.Infect Immun. 2013 Nov;81(11):4280-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00493-13. Epub 2013 Sep 3. Infect Immun. 2013. PMID: 24002068 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct Patterns of Host Adherence by Neisseria gonorrhoeae Isolated from Experimental Gonorrhea.Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2021 May 13;2021:7865405. doi: 10.1155/2021/7865405. eCollection 2021. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34093925 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue Models for Neisseria gonorrhoeae Research-From 2D to 3D.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Feb 11;12:840122. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.840122. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35223556 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Blum H, Beier H, Gross H J. Improved silver staining of plant proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Electrophoresis. 1987;8:93–99.
-
- Brinton C C, Bryan J, Dillon J A. Uses of pili in gonorrhoea control: role of bacterial pili in disease, purification and properties of gonococcal pili, and progress in the development of a gonococcal pilus vaccine for gonorrhoea. In: Gotschlich E C, Holmes K K, Sawyer W D, Young F E, editors. Immunology of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Washington, D.C: American Society for Microbiology; 1978. pp. 155–178.
-
- Fussenegger M, Rudel T, Barten R, Ryll R, Meyer T F. Transformation competence and type-4 pilus biogenesis in Neisseria gonorrhoeae—a review. Gene. 1997;192:125–134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

