Roles of PilC and PilE proteins in pilus-mediated adherence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis to human erythrocytes and endothelial and epithelial cells
- PMID: 9916098
- PMCID: PMC96394
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.67.2.834-843.1999
Roles of PilC and PilE proteins in pilus-mediated adherence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis to human erythrocytes and endothelial and epithelial cells
Abstract
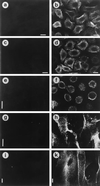
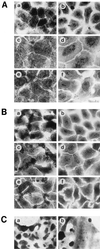
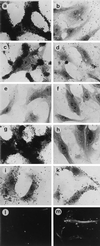
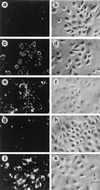
Unlike other type 4 pili, the neisserial pili consist of at least two distinct proteins, the highly variable major subunit PilE forming the pilus fiber and the tip-associated adhesin PilC. PilC protein purified either from gonococci or from Escherichia coli interacted with different human epithelial cell lines, primary epithelial and endothelial cells. The binding of PilC protein efficiently prevented the attachment of piliated Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis to these cell types. Fluorescent beads coated with pili prepared from piliated wild-type N. gonorrhoeae also adhered to these cells, in contrast to beads coated with pili prepared from a piliated PilC-deficient mutant. In the latter case, the binding of fluorescent beads was restored after pretreatment of the pilus-loaded beads with purified PilC. Piliated wild-type N. gonorrhoeae, the piliated PilC-deficient mutant, and N. gonorrhoeae pili assembled in Pseudomonas aeruginosa agglutinated human erythrocytes, while nonpiliated gonococci did not. Consistently, purified PilC did not agglutinate or bind to human erythrocytes, suggesting that N. gonorrhoeae PilE is responsible for pilus-mediated hemagglutination.
Figures

References
-
- Blum H, Beier H, Gross H J. Improved silver staining of plant proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Electrophoresis. 1987;8:93–99.
-
- Brinton C C, Bryan J, Dillon J A. Uses of pili in gonorrhoea control: role of bacterial pili in disease, purification and properties of gonococcal pili, and progress in the development of a gonococcal pilus vaccine for gonorrhoea. In: Gotschlich E C, Holmes K K, Sawyer W D, Young F E, editors. Immunology of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Washington, D.C: American Society for Microbiology; 1978. pp. 155–178.
-
- Fussenegger M, Rudel T, Barten R, Ryll R, Meyer T F. Transformation competence and type-4 pilus biogenesis in Neisseria gonorrhoeae—a review. Gene. 1997;192:125–134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

