Hypoglycemia and impaired hepatic glucose production in mice with a deletion of the C/EBPbeta gene
- PMID: 9916132
- PMCID: PMC407878
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI4243
Hypoglycemia and impaired hepatic glucose production in mice with a deletion of the C/EBPbeta gene
Abstract
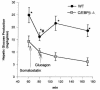
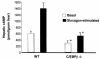
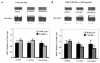
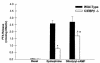
The transcription factor CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta (C/EBPbeta) is enriched in liver and adipose tissue and controls the expression of a wide variety of genes coding for important metabolic pathways, including gluconeogenesis and lipid synthesis. To investigate the role of C/EBPbeta on glucose homeostasis, we studied mice with a targeted deletion of the gene for C/EBPbeta-/- mice. Adult C/EBPbeta-/- mice have hypoglycemia after an 18-hour fast, accompanied by lower hepatic glucose production (40% of that of wild-type mice), with no change in plasma insulin and a lower concentration of plasma free fatty acids (FFA). Glucagon infusion during a pancreatic clamp acutely stimulated hepatic glucose production by 38% in wild-type animals, with no change detected in C/EBPbeta-/- mice. Unexpectedly, both the basal and glucagon-stimulated hepatic cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) levels were lower in C/EBPbeta-/- mice, indicating an essential role for C/EBPbeta in controlling proximal signal transduction. Fasting hypoglycemia was associated with normal levels of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) and glucose-6-phosphatase (G6Pase) gene expression, however net liver glycogenolysis was impaired in C/EBPbeta-/- mice. FFA release from isolated adipose tissue in response to epinephrine was 68% lower in C/EBPbeta-/- mice than in control animals; however, N6,O2'-dibutyryladenosine (Bt2) cAMP stimulated a twofold increase in FFA release in C/EBPbeta-/- compared with no further increase in wild-type mice. Because a deletion in the gene for C/EBPbeta reduces blood glucose and circulating FFA, it could be an important therapeutic target for the treatment of non-insulin-dependent diabetes and possibly obesity, based on designing antagonists that decrease C/EBPbeta activity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The transcription factor CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta regulates gluconeogenesis and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) gene transcription during diabetes.J Biol Chem. 1999 May 7;274(19):13033-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.19.13033. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10224054
-
Mice with a deletion in the gene for CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta have an attenuated response to cAMP and impaired carbohydrate metabolism.J Biol Chem. 2001 Jan 5;276(1):629-38. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M007576200. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11024029
-
Increased insulin receptor substrate-1 and enhanced skeletal muscle insulin sensitivity in mice lacking CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta.J Biol Chem. 2000 May 12;275(19):14173-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.m000764200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10747954
-
Glyceroneogenesis revisited.Biochimie. 2003 Dec;85(12):1199-205. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2003.10.022. Biochimie. 2003. PMID: 14739071 Review.
-
Glucagon and cyclic AMP: time to turn the page?Curr Diabetes Rev. 2012 Sep;8(5):362-81. doi: 10.2174/157339912802083540. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2012. PMID: 22587514 Review.
Cited by
-
GCN2 regulates the CCAAT enhancer binding protein beta and hepatic gluconeogenesis.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2013 Oct 15;305(8):E1007-17. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00063.2013. Epub 2013 Jul 30. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2013. PMID: 23900421 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the Regulation of Hepatic Gluconeogenesis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019 Jan 24;9:802. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00802. eCollection 2018. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 30733709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ETO/MTG8 is an inhibitor of C/EBPbeta activity and a regulator of early adipogenesis.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Nov;24(22):9863-72. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.22.9863-9872.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15509789 Free PMC article.
-
Mice with a deletion in the gene for CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta are protected against diet-induced obesity.Diabetes. 2007 Jan;56(1):161-7. doi: 10.2337/db06-0310. Diabetes. 2007. PMID: 17192478 Free PMC article.
-
C/EBP transcription factors regulate SREBP1c gene expression during adipogenesis.Biochem J. 2009 Dec 14;425(1):215-23. doi: 10.1042/BJ20091112. Biochem J. 2009. PMID: 19811452 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Landschulz WH, Johnson PF, Adashi EY, Graves B J, McKnight SL. Isolation of a recombinant copy of the gene encoding C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1988;2:786–800. - PubMed
-
- Poli V, Mancini FP, Cortese R. IL-6DBP, a nuclear protein involved in interleukin-6 signal transduction, defines a new family of leucine zipper proteins related to C/EBP. Cell. 1990;63:643–653. - PubMed
-
- Williams SC, Cantwell CA, Johnson PF. A family of C/EBP-related proteins capable of forming covalently linked leucine zipper dimers in vitro. Genes Dev. 1991;5:1553–1567. - PubMed
-
- McKnight SL, Lane MD, Gluecksohn-Waelsch S. Is CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein a central regulator of energy metabolism? Genes Dev. 1989;3:2021–2024. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

