Restricted high level expression of Tcf-4 protein in intestinal and mammary gland epithelium
- PMID: 9916915
- PMCID: PMC1853446
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65247-9
Restricted high level expression of Tcf-4 protein in intestinal and mammary gland epithelium
Abstract
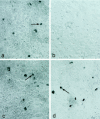
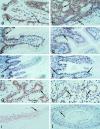
Tcf-4 is a member of the Tcf/Lef family of transcription factors that interact functionally with beta-catenin to mediate Wnt signaling in vertebrates. We have previously demonstrated that the tumor suppressor function of APC in the small intestine is mediated via regulation of Tcf-4/beta-catenin transcriptional activity. To gain further insight into the role of Tcf-4 in development and carcinogenesis we have generated several mouse monoclonal antibodies, one of which is specific for Tcf-4 and another of which recognizes both Tcf-3 and Tcf-4. Immunohistochemistry performed with the Tcf 4- specific monoclonal antibody revealed high levels of expression in normal intestinal and mammary epithelium and carcinomas derived therefrom. Additional sites of Tcf-3 expression, as revealed by staining with the Tcf-3/-4 antibody, occurred only within the stomach epithelium, hair follicles, and keratinocytes of the skin. A temporal Tcf-4 expression gradient was observed along the crypt-villus axis of human small intestinal epithelium: strong Tcf-4 expression was present within the crypts of early (week 16) human fetal small intestine, with the villi showing barely detectable Tcf-4 protein levels. Tcf-4 expression levels increased dramatically on the villi of more highly developed (week 22) fetal small intestine. We conclude that Tcf-4 exhibits a highly restricted expression pattern related to the developmental stage of the intestinal epithelium. The high levels of Tcf-4 expression in mammary epithelium and mammary carcinomas may also indicate a role in the development of this tissue and breast carcinoma.
Figures

References
-
- Molenaar M, van de Wetering M, Oosterwegel M, Peterson-Maduro J, Godsave S, Korinek V, Roose J, Destree O, Clevers H: Xtcf-3 transcription factor mediates β-catenin-induced axis formation in Xenopus embryos. Cell 1996, 86:391-399 - PubMed
-
- Riese J, Yu X, Munnerlyn A, Eresh S, Hsu SC, Grosschedl R, Bienz M: LEF-1, a nuclear factor coordinating signaling inputs from wingless and decapentaplegic. Cell 1997, 88:777-787 - PubMed
-
- Brunner E, Peter O, Schweizer L, Basler K: Pangolin encodes a Lef-1 homologue that acts downstream of Armadillo to transduce the Wingless signal in Drosophila. Nature 1997, 385:829-833 - PubMed
-
- van de Wetering M, Cavallo R, Dooijes D, van Beest M, van Es J, Loureiro A, Ypma D, Hursh D, Jones T, Bejsovec A, Peifer M, Mortin M, Clevers H: Armadillo co-activates transcription driven by the product of the Drosophila segment polarity gene dTCF. Cell 1997, 88:789-799 - PubMed
-
- Behrens J, van Kries JP, Kuehl M, Bruhn D, Wedlich R, Grosschedl R, Birchmeier W: Functional interaction of β-catenin with the transcription factor LEF-1. Nature 1996, 382:638-642 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

