Mortality and causes of death in a Swedish series of systemic sclerosis patients
- PMID: 9924211
- PMCID: PMC1752504
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.57.11.682
Mortality and causes of death in a Swedish series of systemic sclerosis patients
Abstract
Objectives: To analyse survival rates and the causes of death in a systemic sclerosis (SSc) population, and to evaluate the occurrence of fatal malignant neoplasms and their possible association with oral cyclophosphamide (CYC) treatment.
Methods: Survival was calculated for 249 SSc patients followed up for up to 13 years. Mean (SD) follow up was 5.8 (4.2) years. The 49 decreased patients were subdivided according to causes of death and its relation to SSc. Fatal malignancies in CYC treated patients were compared with those occurring in non-CYC treated patients.
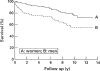
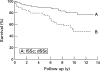
Results: The overall 5 and 10 year survival rates were 86% and 69% respectively. There was a 4.6-fold increased risk of death, as compared with the general population. Prognosis was worse in the diffuse cutaneous involvement (dSSc) and male subgroups than in the limited cutaneous involvement (1SSc) and female subgroups. Of the 49 deaths, 24 were attributable to pulmonary complications such as pulmonary fibrosis, pulmonary hypertension, pneumonia or pulmonary malignancy. Treatment with oral CYC did not increase the risk of dying of cancer.
Conclusions: Mortality is increased both in the SSc population as a whole and in its different subsets (dSSc and 1SSc). Prognosis is worst among male patients with dSSc. However, the 5 year survival rate was better than those reported from earlier studies. Most patients die of cardiopulmonary disease. Five of seven fatal lung cancers were adenocarcinomas, possibly caused by chronic inflammatory disease of the lung. In this study, CYC treatment was not associated with an increased incidence of fatal malignant neoplasms.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oral cyclophosphamide for active scleroderma lung disease: a decision analysis.Med Decis Making. 2008 Nov-Dec;28(6):926-37. doi: 10.1177/0272989X08317015. Epub 2008 Apr 28. Med Decis Making. 2008. PMID: 18443209
-
Survival, causes of death, and risk factors associated with mortality in Spanish systemic sclerosis patients: results from a single university hospital.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2010 Feb;39(4):285-93. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2009.06.002. Epub 2009 Sep 25. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2010. PMID: 19782387
-
Intravenous cyclophosphamide pulse therapy in interstitial lung disease associated with systemic sclerosis in a retrospective open-label study: influence of the extent of inflammation on pulmonary function.Clin Rheumatol. 2018 Oct;37(10):2715-2722. doi: 10.1007/s10067-018-4171-6. Epub 2018 Jul 10. Clin Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 29987427 Free PMC article.
-
[Cancers in systemic sclerosis : risk factors, impact on survival and literature review].Rev Med Interne. 2019 Oct;40(10):637-644. doi: 10.1016/j.revmed.2019.06.004. Epub 2019 Jun 26. Rev Med Interne. 2019. PMID: 31255252 Review. French.
-
Where are we going in the management of interstitial lung disease in patients with systemic sclerosis?Autoimmun Rev. 2015 Jul;14(7):575-8. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2015.02.002. Epub 2015 Feb 21. Autoimmun Rev. 2015. PMID: 25709096 Review.
Cited by
-
The Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis: An Understanding Based on a Common Pathologic Cascade across Multiple Organs and Additional Organ-Specific Pathologies.J Clin Med. 2020 Aug 19;9(9):2687. doi: 10.3390/jcm9092687. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32825112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The clinical significance of serum N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide in systemic sclerosis patients.Clin Rheumatol. 2008 Apr;27(4):437-42. doi: 10.1007/s10067-007-0724-9. Epub 2007 Sep 25. Clin Rheumatol. 2008. PMID: 17899307
-
A data-driven approach finds RNA polymerase III antibody and tendon friction rubs as enrichment tools for early diffuse scleroderma trials.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2023 Apr 3;62(4):1543-1551. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keac501. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2023. PMID: 36031807 Free PMC article.
-
Survival and causes of death in systemic sclerosis patients: a single center registry report from Iran.Rheumatol Int. 2016 Jul;36(7):925-34. doi: 10.1007/s00296-016-3475-6. Epub 2016 Apr 9. Rheumatol Int. 2016. PMID: 27061806
-
Lung cancer and interstitial lung diseases: a systematic review.Pulm Med. 2012;2012:315918. doi: 10.1155/2012/315918. Epub 2012 Jul 29. Pulm Med. 2012. PMID: 22900168 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

