Variation in the composition and pore function of major outer membrane pore protein P2 of Haemophilus influenzae from cystic fibrosis patients
- PMID: 9925510
- PMCID: PMC89055
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.43.2.226
Variation in the composition and pore function of major outer membrane pore protein P2 of Haemophilus influenzae from cystic fibrosis patients
Abstract
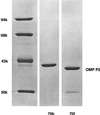
We investigated the relationship between susceptibility to beta-lactam antibiotics and variation in the major outer membrane protein P2 (OmpP2; also called porin) of persistent nonencapsulated Haemophilus influenzae isolated from cystic fibrosis patients. Nine OmpP2 variants were selected from two distinct H. influenzae strains from two patients extensively treated with beta-lactam antibiotics. The variants differed in their susceptibilities to at least two beta-lactam antibiotics. By detergent extraction and column chromatography, OmpP2 was purified from two variants that were derived from strain 70 and that differed notably in their susceptibilities to beta-lactam antibiotics. The proteins were reconstituted into black lipid membranes for measurement of porin function. OmpP2 from the more resistant isolate (isolate 70b) had a smaller channel conductance than OmpP2 of the more susceptible isolate (isolate 70f). DNA sequencing of ompP2 of these isolates revealed single nonsynonymous base differences; there were changes in the amino acid sequence corresponding to surface-exposed loops 4, 5, 6, and 8. Changes in loops 4, 5, and 6 were previously shown to result in antigenic differences. Beside these mutations, variants of strain 70 showed additional mutations in loop 1 and nonexposed loop 3. Taken together, our results suggest that in variants of strain 70, nonsynonymous point mutations accumulated both in the sequences of ompP2 coding for antigen-variable loops and in other loops, notably, loops 1 and 3. The latter changes are suggested to affect the permeability of the porin channel.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Targets of the beta-lactam antibiotics, penicillin-binding proteins, in ampicillin-resistant, non-beta-lactamase-producing Haemophilus influenzae.J Infect Dis. 1992 Jun;165 Suppl 1:S107-9. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165-supplement_1-s107. J Infect Dis. 1992. PMID: 1588136 No abstract available.
-
Mechanism of resistance of an ampicillin-resistant, beta-lactamase-negative clinical isolate of Haemophilus influenzae type b to beta-lactam antibiotics.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jun;25(6):747-53. doi: 10.1128/AAC.25.6.747. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984. PMID: 6611136 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity of beta-lactam resistance-conferring amino acid substitutions in penicillin-binding protein 3 of Haemophilus influenzae.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002 Jul;46(7):2208-18. doi: 10.1128/AAC.46.7.2208-2218.2002. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002. PMID: 12069976 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of beta-lactam resistance in Haemophilus influenzae.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;7(5):610-5. doi: 10.1007/BF01964237. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988. PMID: 3143572 Review.
-
[BLNAR (beta-lactamase-nonproducing ampicillin-resistant Haemophilus influenzae)].Nihon Rinsho. 2003 Mar;61 Suppl 3:176-81. Nihon Rinsho. 2003. PMID: 12717968 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Elimination of channel-forming activity by insertional inactivation of the p13 gene in Borrelia burgdorferi.J Bacteriol. 2002 Dec;184(24):6811-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.24.6811-6819.2002. J Bacteriol. 2002. PMID: 12446631 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple interspecies recombination events documented by whole-genome sequencing in multidrug-resistant Haemophilus influenzae clinical isolates.Access Microbiol. 2024 Feb 12;6(2):000649.v3. doi: 10.1099/acmi.0.000649.v3. eCollection 2024. Access Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38482359 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic profiling of cefotaxime-resistant Haemophilus influenzae from Norway and Sweden reveals extensive expansion of virulent multidrug-resistant international clones.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jul 29;16:1601390. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1601390. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40800114 Free PMC article.
-
Differential expression of porins OmpP2A and OmpP2B of Haemophilus ducreyi.Infect Immun. 2004 Nov;72(11):6271-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.11.6271-6278.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15501753 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Derivation of Fluoroquinolone-Resistant Mutants from Multiple Lineages of Haemophilus influenzae and Identification of Mutations Associated with Fluoroquinolone Resistance.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020 Jan 27;64(2):e01500-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01500-19. Print 2020 Jan 27. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020. PMID: 31740553 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benson S A, Occi J L T, Sampson B A. Mutations that alter the pore function of the OmpF porin of Escherichia coli K12. J Mol Biol. 1988;203:961–970. - PubMed
-
- Burns J L, Smith A L. A major outer-membrane protein functions as a porin in Haemophilus influenzae. J Gen Microbiol. 1987;133:1273–1277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

