A rapid non-culture-based assay for clinical monitoring of phenotypic resistance of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 to lamivudine (3TC)
- PMID: 9925516
- PMCID: PMC89061
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.43.2.264
A rapid non-culture-based assay for clinical monitoring of phenotypic resistance of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 to lamivudine (3TC)
Abstract
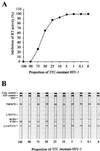
Monitoring for lamivudine (3TC) resistance is important both for the clinical management of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1)-infected patients treated with 3TC and for surveillance of transmission of 3TC-resistant HIV-1. We developed a novel non-culture-based assay for the rapid analysis of phenotypic resistance to 3TC of HIV-1 in plasma. The assay measures the susceptibility of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase (RT) activity to 3TC triphosphate (3TC-TP) in plasma. RT detection was done by the Amp-RT assay, an ultrasensitive PCR-based RT assay. Under our assay conditions, we found that 5 microM 3TC-TP inhibited RT activity from wild-type (WT), zidovudine-resistant, or nevirapine-resistant HIV-1 but not from HIV-1 carrying either the M184V mutation or multidrug (MD) resistance mutations (77L/116Y/151M or 62V/75I/77L/116Y/151M). Mixing experiments showed a detection threshold of 10% 3TC-resistant virus (M184V) in a background of WT HIV-1. To validate the assay for the detection of phenotypic resistance of HIV-1 to 3TC in plasma samples, HIV-1 RT in 30 plasma specimens collected from 15 patients before and during therapy with 3TC was tested for evidence of phenotypic resistance by the Amp-RT assay. The results were compared with those of genotypic analysis. The RT in 12 samples was found to be 3TC sensitive, while the RT in 18 samples had evidence of phenotypic resistance. All 12 samples with 3TC-sensitive RT had WT genotypes at codon 184 and were retrieved before treatment with 3TC. In contrast, all 18 specimens with 3TC-resistant RT were posttherapy samples. This assay provides a simple, rapid, and reliable method for the detection of phenotypic resistance of HIV-1 to 3TC in plasma.
Figures
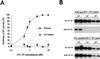



Similar articles
-
Measuring enzymatic HIV-1 susceptibility to two reverse transcriptase inhibitors as a rapid and simple approach to HIV-1 drug-resistance testing.PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e22019. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022019. Epub 2011 Jul 20. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21799767 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid screening of phenotypic resistance to nevirapine by direct analysis of HIV type 1 reverse transcriptase activity in plasma.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1999 Sep 1;15(13):1191-200. doi: 10.1089/088922299310287. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1999. PMID: 10480632
-
Drug resistance and drug combination features of the human immunodeficiency virus inhibitor, BCH-10652 [(+/-)-2'-deoxy-3'-oxa-4'-thiocytidine, dOTC].Antivir Chem Chemother. 2000 Jul;11(4):291-301. doi: 10.1177/095632020001100405. Antivir Chem Chemother. 2000. PMID: 10950391
-
Perspectives on the molecular mechanism of inhibition and toxicity of nucleoside analogs that target HIV-1 reverse transcriptase.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002 Jul 18;1587(2-3):296-9. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4439(02)00092-3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002. PMID: 12084471 Review.
-
Prevalence and incidence of resistance to zidovudine and other antiretroviral drugs.Am J Med. 1997 May 19;102(5B):70-5. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(97)00067-3. Am J Med. 1997. PMID: 9845501 Review.
Cited by
-
Evidence of a role for the Q151L mutation and the viral background in development of multiple dideoxynucleoside-resistant human immunodeficiency virus type 1.J Virol. 2000 Oct;74(20):9339-46. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.20.9339-9346.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 11000201 Free PMC article.
-
Sensitive Pathogen Detection and Drug Resistance Characterization Using Pathogen-Derived Enzyme Activity Amplified by LAMP or CRISPR-Cas.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 1:2024.03.29.24305085. doi: 10.1101/2024.03.29.24305085. medRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38633802 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Quantitation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group O load in plasma by measuring reverse transcriptase activity.J Clin Microbiol. 2000 Jan;38(1):402-5. doi: 10.1128/JCM.38.1.402-405.2000. J Clin Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10618125 Free PMC article.
-
Measuring enzymatic HIV-1 susceptibility to two reverse transcriptase inhibitors as a rapid and simple approach to HIV-1 drug-resistance testing.PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e22019. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022019. Epub 2011 Jul 20. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21799767 Free PMC article.
-
Susceptibility of the porcine endogenous retrovirus to reverse transcriptase and protease inhibitors.J Virol. 2001 Jan;75(2):1048-53. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.2.1048-1053.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11134319 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boucher C A B, Cammack N, Schipper P, Schuurman R, Rouse P, Wainberg M A, Cameron J M. High level resistance to (−) enantiomeric 2′-deoxy-3′-thiacytidine in vitro is due to one amino acid substitution in the catalytic site of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993;37:2231–2234. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Caroline M P, Faulds D. Lamivudine: a review of its antiviral activity, pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic efficacy in the management of HIV infection. Drugs. 1997;53:657–680. - PubMed
-
- Carpenter C C, Fischl M A, Hammer S M, Hirsch M S, Jacobsen D M, Katzenstein D A, Montaner J S, Richman D D, Saag M S, Schooley R T, Thompson M A, Vella S, Yeni P G, Volberding P A. Antiviral therapy for HIV infection in 1997: updated recommendations of the International AIDS Society—USA panel. JAMA. 1997;277:1962–1969. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

