Staphylokinase as a plasminogen activator component in recombinant fusion proteins
- PMID: 9925575
- PMCID: PMC91054
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.65.2.506-513.1999
Staphylokinase as a plasminogen activator component in recombinant fusion proteins
Abstract
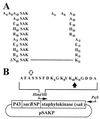
The plasminogen activator staphylokinase (SAK) is a promising thrombolytic agent for treatment of myocardial infarction. It can specifically stimulate the thrombolysis of both erythrocyte-rich and platelet-rich clots. However, SAK lacks fibrin-binding and thrombin inhibitor activities, two functions which would supplement and potentially improve its thrombolytic potency. Creating a recombinant fusion protein is one approach for combining protein domains with complementary functions. To evaluate SAK for use in a translational fusion protein, both N- and C-terminal fusions to SAK were constructed by using hirudin as a fusion partner. Recombinant fusion proteins were secreted from Bacillus subtilis and purified from culture supernatants. The rate of plasminogen activation by SAK was not altered by the presence of an additional N- or C-terminal protein sequence. However, cleavage at N-terminal lysines within SAK rendered the N-terminal fusion unstable in the presence of plasmin. The results of site-directed mutagenesis of lysine 10 and lysine 11 in SAK suggested that a plasmin-resistant variant cannot be created without interfering with the plasmin processing necessary for activation of SAK. Although putative plasmin cleavage sites are located at the C-terminal end of SAK at lysine 135 and lysine 136, these sites were resistant to plasmin cleavage in vitro. Therefore, C-terminal fusions represent stable configurations for developing improved thrombolytic agents based on SAK as the plasminogen activator component.
Figures



References
-
- Behnke D, Gerlach D. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, and Streptococcus sanguis of a gene for staphylokinase—a bacterial plasminogen activator. Mol Gen Genet. 1987;210:528–534. - PubMed
-
- Bode C, Hudelmayer M, Mehwald P, Bauer S, Freitag M, von Hodenberg E, Newell J B, Kubler W, Haber E, Runge M S. Fibrin-targeted recombinant hirudin inhibits fibrin deposition on experimental clots more efficiently than recombinant hirudin. Circulation. 1994;90:1956–1963. - PubMed
-
- Bode C, Runge M S, Schonermark S, Eberle T, Newell J B, Kubler W, Haber E. Conjugation to antifibrin Fab′ enhances fibrinolytic potency of single-chain urokinase plasminogen activator. Circulation. 1990;81:1974–1980. - PubMed
-
- Chan, D. W., C. J. Veillette, and S. P. Lees-Miller. Autophosphorylation sites in the human Ku antoantigen. Submitted for publication.
-
- Chang J Y. Production, properties, and thrombin inhibitory mechanism of hirudin amino-terminal core fragments. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:22159–22166. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

