Role of microcystins in poisoning and food ingestion inhibition of Daphnia galeata caused by the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa
- PMID: 9925609
- PMCID: PMC91088
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.65.2.737-739.1999
Role of microcystins in poisoning and food ingestion inhibition of Daphnia galeata caused by the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa
Abstract
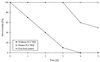
The effects of microcystins on Daphnia galeata, a typical filter-feeding grazer in eutrophic lakes, were investigated. To do this, the microcystin-producing wild-type strain Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806 was compared with a mcy- PCC7806 mutant, which could not synthesize any variant of microcystin due to mutation of a microcystin synthetase gene. The wild-type strain was found to be poisonous to D. galeata, whereas the mcy- mutant did not have any lethal effect on the animals. Both variants of PCC7806 were able to reduce the Daphnia ingestion rate. Our results suggest that microcystins are the most likely cause of the daphnid poisoning observed when wild-type strain PCC7806 is fed to the animals, but these toxins are not responsible for inhibition of the ingestion process.
Figures

References
-
- Balushkina E W, Winberg G G. Relation between length and body weight of plankton crustacean. In: Winberg G G, editor. Biological base in lake productivity determination. Leningrad, USSR: Zoological Institute Press; 1979. pp. 58–79.
-
- Barry B A, Boerner R J, de Paula J C. The use of cyanobacteria in the study of the structure and function of photosystem II. In: Bryant D A, editor. The molecular biology of cyanobacteria. Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers; 1994. pp. 217–257.
-
- Benndorf J, Henning M. Daphnia and toxic blooms of Microcystis aeruginosa in Bautzen reservoir (GDR) Int Rev Gesamten Hydrobiol. 1989;74:233–248.
-
- Carmichael W W. Cyanobacteria secondary metabolites—the cyanotoxins. J Appl Bacteriol. 1992;72:445–459. - PubMed
-
- Codd G A. Cyanobacterial toxins: occurrence, properties and biological significance. Water Sci Technol. 1995;32:149–156.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

