Evaluation of toxic effects of aeration and trichloroethylene oxidation on methanotrophic bacteria grown with different nitrogen sources
- PMID: 9925614
- PMCID: PMC91093
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.65.2.766-772.1999
Evaluation of toxic effects of aeration and trichloroethylene oxidation on methanotrophic bacteria grown with different nitrogen sources
Abstract
In this study we evaluated specific and nonspecific toxic effects of aeration and trichloroethylene (TCE) oxidation on methanotrophic bacteria grown with different nitrogen sources (nitrate, ammonia, and molecular nitrogen). The specific toxic effects, exerted directly on soluble methane monooxygenase (sMMO), were evaluated by comparing changes in methane uptake rates and naphthalene oxidation rates following aeration and/or TCE oxidation. Nonspecific toxic effects, defined as general cellular damage, were examined by using a combination of epifluorescent cellular stains to measure viable cell numbers based on respiratory activity and measuring formate oxidation activities following aeration and TCE transformation. Our results suggest that aeration damages predominantly sMMO rather than other general cellular components, whereas TCE oxidation exerts a broad range of toxic effects that damage both specific and nonspecific cellular functions. TCE oxidation caused sMMO-catalyzed activity and respiratory activity to decrease linearly with the amount of substrate degraded. Severe TCE oxidation toxicity resulted in total cessation of the methane, naphthalene, and formate oxidation activities and a 95% decrease in the respiratory activity of methanotrophs. The failure of cells to recover even after 7 days of incubation with methane suggests that cellular recovery following severe TCE product toxicity is not always possible. Our evidence suggests that generation of greater amounts of sMMO per cell due to nitrogen fixation may be responsible for enhanced TCE oxidation activities of nitrogen-fixing methanotrophs rather than enzymatic protection mechanisms associated with the nitrogenase enzymes.
Figures
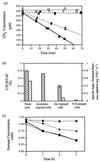
 , fresh cells;
, fresh cells;
 , acetylene-exposed cells;
, acetylene-exposed cells;
 , air-exposed cells; ∗,
TCE-exposed cells. (b)
, air-exposed cells; ∗,
TCE-exposed cells. (b)
 , CTC/DTAF ratios;
, CTC/DTAF ratios;
 , naphthalene
oxidation rates. VSS, volatile suspended solids; d, day.
, naphthalene
oxidation rates. VSS, volatile suspended solids; d, day.
 ,
naphthalene oxidation rates. d, day.
,
naphthalene oxidation rates. d, day.
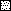 ,
CH4 uptake rates;
,
CH4 uptake rates;
 , naphthalene
oxidation rates.
, naphthalene
oxidation rates.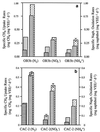
 , CH4
uptake rates of TCE-free cells;
, CH4
uptake rates of TCE-free cells;
 ,
CH4 uptake rates of TCE-exposed cells;
,
CH4 uptake rates of TCE-exposed cells;
 , naphthalene
oxidation rates of TCE-free cells;
, naphthalene
oxidation rates of TCE-free cells;
 ,
naphthalene oxidation rates of TCE-exposed cells. d, day.
,
naphthalene oxidation rates of TCE-exposed cells. d, day.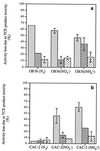
 , CH4
uptake rates;
, CH4
uptake rates;  ,
naphthalene oxidation rates; ▩, CTC/DTAF ratios.
,
naphthalene oxidation rates; ▩, CTC/DTAF ratios.

References
-
- Bhupathiraju, V., M. Hernandez, D. Landfear, and L. Alvarez-Cohen. Application of a tetrazolium dye as an indicator of viability in anaerobic bacteria. Submitted for publication. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

