A novel chromogenic ester agar medium for detection of Salmonellae
- PMID: 9925620
- PMCID: PMC91099
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.65.2.807-812.1999
A novel chromogenic ester agar medium for detection of Salmonellae
Abstract
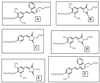
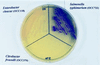
A novel agar medium, chromogenic Salmonella esterase (CSE) agar, for the differentiation of salmonellae is described. The agar contains peptones and nutrient extracts together with the following (grams per liter unless otherwise specified): 4-[2-(4-octanoyloxy-3, 5-dimethoxyphenyl)-vinyl]-quinolinium-1-(propan-3-yl carboxylic acid) bromide (SLPA-octanoate; bromide form), 0.3223; lactose, 14. 65; trisodium citrate dihydrate, 0.5; Tween 20, 3.0; ethyl 4-dimethylaminobenzoate, 0.035% (wt/vol), novobiocin, 70 mg liter-1. The key component of the medium is SLPA-octanoate, a newly synthesized ester formed from a C8 fatty acid and a phenolic chromophore. In CSE agar, the ester is hydrolyzed by Salmonella spp. to yield a brightly colored phenol which remains tightly bound within colonies. After 24 h of incubation at 37 or 42 degreesC, colonies of typical Salmonella spp. were burgundy colored on a transparent yellow background, whereas non-Salmonella spp. were white, cream, yellow or transparent. CSE agar was evaluated by using a panel of strains including a high proportion of Salmonella and non-Salmonella strains giving atypical reactions on other differential agars. The sensitivity (93.1%) of CSE agar for non-typhi salmonellae compared favorably with those of Rambach (82. 8%), xylose-lysine-deoxycholate (XLD; 91.4%), Hektoen-enteric (89.7%), and SM ID (91.4%) agars. The specificity (93.9%) was also comparable to those of other Salmonella media (SM ID agar, 95.9%; Rambach agar, 91.8%; XLD agar, 91.8%; Hektoen-enteric agar, 87.8%). Strains of Citrobacter freundii and Proteus spp. giving false-positive reactions with other media gave a negative color reaction on CSE agar. CSE agar enabled the detection of >30 Salmonella serotypes, including agona, anatum, enteritidis, hadar, heidelberg, infantis, montevideo, thompson, typhimurium, and virchow, which accounted for 91.8% of the salmonella isolates recorded by the Public Health Laboratory Service (Colindale, London, England) for 1997.
Figures
References
-
- Aamlid K H, Lee G, Price R G, Richardson A C, Smith B V, Taylor S A. Development of improved chromogenic substrates for the detection and assay of hydrolytic enzymes. Chem. Ind. (London) 1989. pp. 106–108.
-
- Anonymous. The Oxoid manual. Basingstoke, Hampshire, United Kingdom: Oxoid Ltd.; 1990.
-
- Entis P. Improved hydrophobic grid membrane filter method, using EF-18 agar, for detection of Salmonella in foods: collaborative study. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1990;73:734–742. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

