Protein 4.1R-deficient mice are viable but have erythroid membrane skeleton abnormalities
- PMID: 9927493
- PMCID: PMC407893
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI3858
Protein 4.1R-deficient mice are viable but have erythroid membrane skeleton abnormalities
Abstract
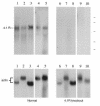
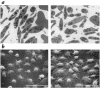
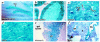
A diverse family of protein 4.1R isoforms is encoded by a complex gene on human chromosome 1. Although the prototypical 80-kDa 4.1R in mature erythrocytes is a key component of the erythroid membrane skeleton that regulates erythrocyte morphology and mechanical stability, little is known about 4.1R function in nucleated cells. Using gene knockout technology, we have generated mice with complete deficiency of all 4.1R protein isoforms. These 4.1R-null mice were viable, with moderate hemolytic anemia but no gross abnormalities. Erythrocytes from these mice exhibited abnormal morphology, lowered membrane stability, and reduced expression of other skeletal proteins including spectrin and ankyrin, suggesting that loss of 4. 1R compromises membrane skeleton assembly in erythroid progenitors. Platelet morphology and function were essentially normal, indicating that 4.1R deficiency may have less impact on other hematopoietic lineages. Nonerythroid 4.1R expression patterns, viewed using histochemical staining for lacZ reporter activity incorporated into the targeted gene, revealed focal expression in specific neurons in the brain and in select cells of other major organs, challenging the view that 4.1R expression is widespread among nonerythroid cells. The 4.1R knockout mice represent a valuable animal model for exploring 4.1R function in nonerythroid cells and for determining pathophysiological sequelae to 4.1R deficiency.
Figures

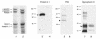


References
-
- Anderson RA, Correas I, Mazzucco C, Castle JD, Marchesi VT. Tissue-specific analogues of erythrocyte protein 4.1 retain functional domains. J Cell Biochem. 1988;37:269–284. - PubMed
-
- Granger BL, Lazarides E. Membrane skeletal protein 4.1 of avian erythrocytes is composed of multiple variants that exhibit tissue-specific expression. Cell. 1984;37:595–607. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

