The common cytokine receptor gamma chain and the pre-T cell receptor provide independent but critically overlapping signals in early alpha/beta T cell development
- PMID: 9927518
- PMCID: PMC2192922
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.189.3.563
The common cytokine receptor gamma chain and the pre-T cell receptor provide independent but critically overlapping signals in early alpha/beta T cell development
Abstract
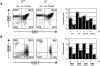
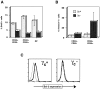
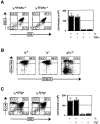
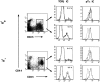
Intracellular signals emanating from cytokine and antigen receptors are integrated during the process of intrathymic development. Still, the relative contributions of cytokine receptor signaling to pre-T cell receptor (TCR) and TCR-mediated differentiation remain undefined. Interleukin (IL)-7 interactions with its cognate receptor complex (IL-7Ralpha coupled to the common cytokine receptor gamma chain, gammac) play a dominant role in early thymopoiesis. However, alpha/beta T cell development in IL-7-, IL-7Ralpha-, and gammac-deficient mice is only partially compromised, suggesting that additional pathways can rescue alpha/beta T lineage cells in these mice. We have investigated the potential interdependence of gammac- and pre-TCR-dependent pathways during intrathymic alpha/beta T cell differentiation. We demonstrate that gammac-dependent cytokines do not appear to be required for normal pre-TCR function, and that the rate-limiting step in alpha/beta T cell development in gammac- mice does not involve TCR-beta chain rearrangements, but rather results from poor maintenance of early thymocytes. Moreover, mice double mutant for both gammac and pre-Talpha show vastly reduced thymic cellularity and a complete arrest of thymocyte differentiation at the CD44(+)CD25(+) cell stage. These observations demonstrate that the pre-TCR provides the gammac-independent signal which allows alpha/beta T cell development in gammac- mice. Thus, a series of overlapping signals derived from cytokine and T cell receptors guide the process of alpha/beta thymocyte development.
Figures



References
-
- Sugamura K, Asao H, Kondo M, Tanaka N, Ishii N, Nakamura M, Takeshita T. The common gamma-chain for multiple cytokine receptors. Adv Immunol. 1995;59:225–277. - PubMed
-
- Leonard WJ. Dysfunctional cytokine receptor signaling in severe combined immunodeficiency. J Investig Med. 1996;44:304–311. - PubMed
-
- Sugamura K, Asao H, Kondo M, Tanaka N, Ishii N, Ohbo K, Nakamura M, Takeshita T. The interleukin-2 receptor γ chain: its role in multiple cytokine receptor complexes and T cell development in XSCID. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:179–205. - PubMed
-
- Cao X, Shores EW, Hu LJ, Anver MR, Kelsall BL, Russell SM, Drago J, Noguchi M, Grinberg A, Bloom ET, et al. Defective lymphoid development in mice lacking expression of the common cytokine receptor gamma chain. Immunity. 1995;2:223–238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

