Expression cloning of LDLB, a gene essential for normal Golgi function and assembly of the ldlCp complex
- PMID: 9927668
- PMCID: PMC15325
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.3.915
Expression cloning of LDLB, a gene essential for normal Golgi function and assembly of the ldlCp complex
Abstract
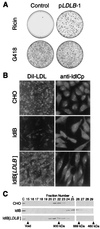
The Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell mutants ldlC and ldlB, which exhibit almost identical phenotypes, define two genes required for multiple steps in the normal medial and trans Golgi-associated processing of glycoconjugates. The LDLC gene encodes ldlCp, an approximately 80-kDa protein, which in wild-type, but not ldlB, cells associates reversibly with the cytoplasmic surface of the Golgi apparatus. Here, we have used a retrovirus-based expression cloning system to clone a murine cDNA, LDLB, that corrects the pleiotropic mutant phenotypes of ldlB cells. The corresponding mRNA was not detected in ldlB mutants. LDLB encodes an approximately 110-kDa protein, ldlBp, which lacks homology to known proteins and contains no common structural motifs. Database searches identified short segments of homology to sequences from Drosophila melanogaster, Arabidopsis thaliana, and Caenorhabditis elegans, and the essentially full-length homologous human sequence (82% identity); however, as was the case for ldlCp, no homologue was identified in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. We have found that in wild-type cell cytosols, ldlCp is a component of an approximately 950-kDa "ldlCp complex," which is smaller, approximately 700 kDa, in ldlB cytosols. Normal assembly of this complex is ldlBp-dependent and may be required for Golgi association of ldlCp and for the normal activities of multiple luminal Golgi processes.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

