Neuroligin 1 is a postsynaptic cell-adhesion molecule of excitatory synapses
- PMID: 9927700
- PMCID: PMC15357
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.3.1100
Neuroligin 1 is a postsynaptic cell-adhesion molecule of excitatory synapses
Abstract
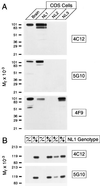
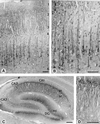
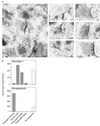
At the synapse, presynaptic membranes specialized for vesicular traffic are linked to postsynaptic membranes specialized for signal transduction. The mechanisms that connect pre- and postsynaptic membranes into synaptic junctions are unknown. Neuroligins and beta-neurexins are neuronal cell-surface proteins that bind to each other and form asymmetric intercellular junctions. To test whether the neuroligin/beta-neurexin junction is related to synapses, we generated and characterized monoclonal antibodies to neuroligin 1. With these antibodies, we show that neuroligin 1 is synaptic. The neuronal localization, subcellular distribution, and developmental expression of neuroligin 1 are similar to those of the postsynaptic marker proteins PSD-95 and NMDA-R1 receptor. Quantitative immunogold electron microscopy demonstrated that neuroligin 1 is clustered in synaptic clefts and postsynaptic densities. Double immunofluorescence labeling revealed that neuroligin 1 colocalizes with glutamatergic but not gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic synapses. Thus neuroligin 1 is a synaptic cell-adhesion molecule that is enriched in postsynaptic densities where it may recruit receptors, channels, and signal-transduction molecules to synaptic sites of cell adhesion. In addition, the neuroligin/beta-neurexin junction may be involved in the specification of excitatory synapses.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

