Circulating soluble factor-inhibiting natural killer (NK) activity of fresh peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) patients
- PMID: 9933422
- PMCID: PMC1905197
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.00741.x
Circulating soluble factor-inhibiting natural killer (NK) activity of fresh peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) patients
Abstract
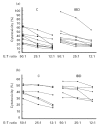
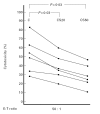
This study was performed in order to assess the cytotoxic activity, both natural (NK) and antibody-dependent (ADCC), of PBMC from 38 IBD patients and correlate it with their clinical features. Cytotoxicity assays were performed using sensitive target cells for NK and ADCC activities. In some experiments, highly purified NK cells, obtained both by Percoll density gradient and by co-culturing non-adherent PBMC with RPMI 8866 feeder cells, were used as effector cells. Furthermore, we evaluated NK cell parameters such as number, surface expression of adhesion molecules (CD11a/CD18, CD49d and CD54) and response to different stimuli. We observed a decreased NK cytotoxicity of PBMC from IBD patients, both in ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn's disease (CD), independently of the clinical activity of disease. In contrast, the ADCC lytic activity was within normal range. The lower NK cytotoxic activity observed in our IBD patients cannot be related to a decreased number of NK cells, surface expression of adhesion molecules, defective response to IL-2 and maturative defect. Decreased NK activity was induced in PBMC of controls when serum of patients was added and this was unrelated to monocyte-derived modulating factor(s). Our data show a decreased natural killing by fresh PBMC from IBD patients. This lower activity seems to be unrelated to a primary NK cell defect, since purified NK cells exhibited normal levels of killing. It might be hypothesized that serum factors, possibly derived from lymphocytes, with inhibitory properties on NK activity, might be functionally active in the blood of IBD patients, thus modulating NK activity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dysregulation of Metabolic Pathways in Circulating Natural Killer Cells Isolated from Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients.J Crohns Colitis. 2021 Aug 2;15(8):1316-1325. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjab014. J Crohns Colitis. 2021. PMID: 33460436 Free PMC article.
-
NK cells stimulated with IL-15 or CpG ODN enhance rituximab-dependent cellular cytotoxicity against B-cell lymphoma.Exp Hematol. 2008 Jan;36(1):69-77. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2007.08.012. Epub 2007 Oct 23. Exp Hematol. 2008. PMID: 17959301
-
Within peripheral blood mononuclear cells, antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity of rituximab-opsonized Daudi cells is promoted by NK cells and inhibited by monocytes due to shaving.J Immunol. 2008 Aug 15;181(4):2916-24. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.4.2916. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18684983
-
Lysis of pig endothelium by IL-2 activated human natural killer cells is inhibited by swine and human major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I gene products.Ann Transplant. 1997;2(1):14-20. Ann Transplant. 1997. PMID: 9869836
-
IL-2 rapidly induces natural killer cell adhesion to human endothelial cells. A potential mechanism for endothelial injury.J Immunol. 1988 Jul 1;141(1):158-63. J Immunol. 1988. PMID: 3259966
Cited by
-
Psoriasis and inflammatory bowel disease: links and risks.Psoriasis (Auckl). 2016 Jul 20;6:73-92. doi: 10.2147/PTT.S85194. eCollection 2016. Psoriasis (Auckl). 2016. PMID: 29387596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Loss of cytomegalovirus-specific immunological memory in a patient with thymoma.Clin Exp Immunol. 2002 Aug;129(2):297-301. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2002.01923.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12165086 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of Metabolic Pathways in Circulating Natural Killer Cells Isolated from Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients.J Crohns Colitis. 2021 Aug 2;15(8):1316-1325. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjab014. J Crohns Colitis. 2021. PMID: 33460436 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Killer Cell Immunoglobulin-Like Receptor Genes and Their HLA Ligands in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases.J Immunol Res. 2020 Sep 19;2020:4873648. doi: 10.1155/2020/4873648. eCollection 2020. J Immunol Res. 2020. PMID: 33015197 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic and Functional Changes in Peripheral Blood Natural Killer Cells in Crohn Disease Patients.Mediators Inflamm. 2020 Feb 19;2020:6401969. doi: 10.1155/2020/6401969. eCollection 2020. Mediators Inflamm. 2020. PMID: 32148442 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Raedler A, Schreiber S, Weerth A, Voss A, Peters S, Greten H. Assessment of in vivo activated T cells in patients with Crohn's disease. Hepato Gastroenterol. 1990;37:67–71. - PubMed
-
- Pallone F, Fais S, Squarcia O, Biancone L, Pozzilli P, Boirivant M. Activation of peripheral blood and lamina propria lymphocytes in Crohn's disease In vivo state of activation and in vitro response to stimulation as defined by the expression of early activation antigens. Gut. 1987;28:745–53. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

