Administration of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) in vivo--down-regulatory effects on the IL-1 system
- PMID: 9933433
- PMCID: PMC1905185
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.00757.x
Administration of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) in vivo--down-regulatory effects on the IL-1 system
Abstract
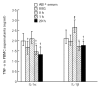
Modulation of the cytokine network may be of importance for the beneficial effects of therapy with IVIG seen in a wide range of immune-mediated disorders. In the present study we investigate the effect of IVIG administration in vivo on the IL-1 system in 12 patients with primary hypogammaglobulinaemia. Before IVIG infusion these patients had significantly elevated levels of IL-1alpha and IL-1beta both in plasma and in supernatants from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) compared with healthy controls. After one bolus infusion with IVIG (0.4 g/kg) we found a significant change in the profile of the components of the IL-1 system: a marked increase in levels of IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) and neutralizing antibodies against IL-1alpha, a moderate decrease in levels of IL-1alpha, IL-1beta and soluble (s) IL-1 receptor type I and a significant increase in sIL-1 receptor type II levels. These changes were found both in plasma and in PBMC isolated after IVIG administration. Furthermore, pooled serum obtained after IVIG infusion suppressed lipopolysaccharide- and staphylococcal enterotoxin B-stimulated, but not phorbol myristate acetate-stimulated, release of IL-1alpha and IL-1beta from PBMC isolated from healthy controls. Finally, these changes in circulating levels of various IL-1 modulators after IVIG infusion appeared to cause a significantly impaired ability of IL-1 to stimulate PBMC for tumour necrosis factor-alpha release. Our findings suggest that IVIG administration may not only down-regulate the activity in the IL-1 system, but also hamper IL-1 stimulation of PBMC.
Figures

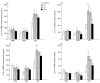
References
-
- Dwyer JM. Manipulating the immune system with immune globulin. N Engl J Med. 1992;326:107–16. - PubMed
-
- Mobini N, Sarela A, Ahmed AR. Intravenous immunoglobulins in the therapy of autoimmune and systemic inflammatory disorders. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1995;74:119–28. - PubMed
-
- Dalakas MC. Intravenous immune globulin therapy for neurologic disease. Ann Intern Med. 1997;126:721–30. - PubMed
-
- Wolf HM, Eibl MM. Immunomodulatory effect of immunoglobulins. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1996;14(Suppl. 15):S17–S25. - PubMed
-
- Ballow M. Mechanisms of action of intravenous immune serum globulin in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997;100:151–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

