High IgE in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients is complexed with anti-IgE autoantibodies
- PMID: 9933440
- PMCID: PMC1905175
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.00787.x
High IgE in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients is complexed with anti-IgE autoantibodies
Abstract
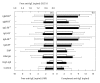
This study presents data on more than 300 RA and allergic patients analysed for their serum levels of anti-immunoglobulin isotype autoantibodies and IgE. We observed high levels of IgE in sera of RA and allergic patients. Interestingly, we measured significantly higher specific IgE levels against Alternaria but not against nine other allergens in the RA compared with the allergic group. As expected, anti-IgG autoantibodies (rheumatoid factors (RF)) of different isotypes were detected in sera from RA patients only. However, we found increased titres of complexed anti-IgE autoantibodies in all RF+ groups and in the allergic group. These findings may explain why despite elevated IgE levels a decreased prevalence of allergic diseases in RA patients has been observed.
Figures

References
-
- Goronzy JJ, Weyand CM. T and B cell-dependent pathways in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 1995;7:214–21. - PubMed
-
- Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988;31:315–24. - PubMed
-
- Paimela L, Palasuo T, Leirisalo-Repo M, Helve T, Aho K. Prognostic value of quantitative measurements of rheumatoid factors in early rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1995;34:1146–50. - PubMed
-
- Van Zeben D, Hazes JM, Zwinderman AH, Vandenbroucke JP, Breedveld FC. Factors predicting outcome of rheumatoid arthritis: results of a follow-up study. J Rheumatol. 1993;20:1288–96. - PubMed
-
- Houssien DA, Jonsson T, Davies E, Scott DL. Clinical significance of IgA rheumatoid factor subclasses in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1997;24:2119–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

