Mononuclear cell subpopulations in preterm and full-term neonates: independent effects of gestational age, neonatal infection, maternal pre-eclampsia, maternal betamethason therapy, and mode of delivery
- PMID: 9933458
- PMCID: PMC1905151
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.00795.x
Mononuclear cell subpopulations in preterm and full-term neonates: independent effects of gestational age, neonatal infection, maternal pre-eclampsia, maternal betamethason therapy, and mode of delivery
Abstract
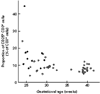
Blood samples from 29 preterm (24-32 weeks of gestation) and 21 full-term (37-42 weeks of gestation) neonates were analysed for surface markers of lymphocyte subtypes and macrophages, and the effects of gestational age, neonatal infection, maternal pre-eclampsia, maternal betamethason therapy and mode of delivery were assessed with multiple regression analysis. Gestational age alone had few independent effects (increase in CD3+, CD8+CD45RA+, and CD11alpha+ cells, and decrease in CD14+, HLA-DR- cells) during the third trimester on the proportions of the immune cell subtypes studied. Neonatal infection and mother's pre-eclampsia had the broadest and very opposite kinds of effects on the profile of immune cells in the blood. Infection of the neonate increased the proportions of several 'immature' cells (CD11alpha-CD20+, CD40+CD19-, and CD14+HLA-DR-), whereas mother's pre-eclampsia decreased the proportions of naive cell types (CD4+CD8+, CD5+CD19+). In addition, neonatal infection increased the proportion of T cells (CD3+, CD3+CD25+, and CD4+/CD8+ ratio, and CD45RA+ cells), while maternal pre-eclampsia had a decreasing effect on the proportion of CD4+ cells, CD4+/CD8+ ratio, and proportions of CD11alpha+, CD14+ and CD14+HLA-DR+ cells. Maternal betamethason therapy increased the proportion of T cells (CD3+) and macrophages (CD14+, CD14+HLA-DR+), but decreased the proportion of natural killer (NK) cells. Caesarean section was associated with a decrease in the proportion of CD14+ cells. We conclude that the 'normal range' of proportions of different mononuclear cells is wide during the last trimester; further, the effect of gestational age on these proportions is more limited than the effects of other neonatal and even maternal factors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Two-color flow cytometric analysis of preterm and term newborn lymphocytes.Immunobiology. 2000 Nov;202(5):421-8. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(00)80101-1. Immunobiology. 2000. PMID: 11205372
-
Lymphocyte subpopulations in pregnancy complicated by hypertension.J Obstet Gynaecol. 2003 Jan;23(1):20-6. doi: 10.1080/0144361021000043163. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2003. PMID: 12623476
-
Expression of lymphocyte activation markers of preterm neonates is associated with perinatal complications.BMC Immunol. 2016 Jun 21;17(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s12865-016-0159-7. BMC Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27328920 Free PMC article.
-
Infection determinants at extremes of age.J Antimicrob Chemother. 1994 Aug;34 Suppl A:1-9. doi: 10.1093/jac/34.suppl_a.1. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1994. PMID: 7844065 Review.
-
The Genetic Background of Neonatal Disease.Neonatology. 2018;113(4):400-405. doi: 10.1159/000487619. Epub 2018 May 31. Neonatology. 2018. PMID: 29852489 Review.
Cited by
-
Active immunization of premature and low birth-weight infants: a review of immunogenicity, efficacy, and tolerability.Paediatr Drugs. 2007;9(1):17-32. doi: 10.2165/00148581-200709010-00003. Paediatr Drugs. 2007. PMID: 17291134 Review.
-
Lymphocyte subsets in term and significantly preterm UK infants in the first year of life analysed by single platform flow cytometry.Clin Exp Immunol. 2005 May;140(2):289-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02767.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15807853 Free PMC article.
-
Flow cytometric measurement of HLA-DR expression on circulating monocytes in healthy and sick neonates using monocyte negative selection.Clin Exp Immunol. 2001 Mar;123(3):402-7. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2001.01471.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11298126 Free PMC article.
-
[Effect of perinatal factors on postnatal development of lymphocyte subsets in early preterm infants].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2016 Oct;18(10):953-959. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2016.10.007. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27751210 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Prenatal and Perinatal Environmental Influences Shaping the Neonatal Immune System: A Focus on Asthma and Allergy Origins.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Apr 9;18(8):3962. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18083962. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33918723 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hayward AR. Development of lymphocyte responses and interactions in the human fetus and newborn. Immunol Rev. 1981;57:39–60. - PubMed
-
- Burgio GR, Hanson LA, Ugazio A. Immunology of the neonate. Berlin: Springer; 1987.
-
- Lucivero G, D'Addario V, Tannoia N, Dell'Osso A, Gambatesa V, Lopalco PL, Cagnazzo G. Ontogeny of human lymphocytes. Two-color fluorescence analysis of circulating lymphocyte subsets in fetuses in the second trimester of pregnancy. Fetal Diagn and Ther. 1991;6:101–6. - PubMed
-
- Baker DA, Hameed C, Tejani N, Thomas J, Dattwyler R. Lymphocyte subsets in the neonates of preeclamptic mothers. Am J Reprod Immunol Microbiol. 1987;14:107–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

