Reg1ulatory role and molecular interactions of a cell-surface heparan sulfate proteoglycan (N-syndecan) in hippocampal long-term potentiation
- PMID: 9952400
- PMCID: PMC6786044
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-04-01226.1999
Reg1ulatory role and molecular interactions of a cell-surface heparan sulfate proteoglycan (N-syndecan) in hippocampal long-term potentiation
Abstract
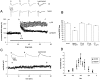
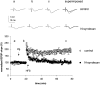
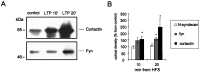
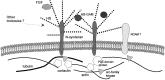
The cellular mechanisms responsible for synaptic plasticity involve interactions between neurons and the extracellular matrix. Heparan sulfates (HSs) constitute a group of glycosaminoglycans that accumulate in the beta-amyloid deposits in Alzheimer's disease and influence the development of neuron-target contacts by interacting with other cell surface and matrix molecules. However, the contribution of HSs to brain function is unknown. We found that HSs play a crucial role in long-term potentiation (LTP), a finding that is consistent with the idea that converging molecular mechanisms are used in the development of neuron-target contacts and in activity-induced synaptic plasticity in adults. Enzymatic cleavage of HS by heparitinase as well as addition of soluble heparin-type carbohydrates prevented expression of LTP in response to 100 Hz/1 sec stimulation of Schaffer collaterals in rat hippocampal slices. A prominent carrier protein for the type of glycans implicated in LTP regulation in the adult hippocampus was identified as N-syndecan (syndecan-3), a transmembrane proteoglycan that was expressed at the processes of the CA1 pyramidal neurons in an activity-dependent manner. Addition of soluble N-syndecan into the CA1 dendritic area prevented tetanus-induced LTP. A major substrate of src-type kinases, cortactin (p80/85), and the tyrosine kinase fyn copurified with N-syndecan from hippocampus. Moreover, association of both cortactin and fyn to N-syndecan was rapidly increased after induction of LTP. N-syndecan may thus act as an important regulator in the activity-dependent modulation of neuronal connectivity by transmitting signals between extracellular heparin-binding factors and the fyn signaling pathway.
Figures





References
-
- Abe K, Saito H. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors, herbimycin A and lavendustin A, block formation of long-term potentiation in the dentate gyrus in vivo. Brain Res. 1993;621:167–170. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong R, Montiminy M. Transsynaptic control of gene expression. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1993;16:17–29. - PubMed
-
- Bame KJ, Danda J, Hassall A, Tumova S. Aβ(1–40) prevents heparanase-catalyzed degradation of heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycans and proteoglycans in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:17005–17011. - PubMed
-
- Bernfield M, Kokenyesi R, Kato M, Hinkes MT, Spring J, Gallo RL, Lose EJ. Biology of the syndecans: a family of transmembrane heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:365–393. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
