In vitro biosynthesis of phosphorylated starch in intact potato amyloplasts
- PMID: 9952440
- PMCID: PMC32121
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.119.2.455
In vitro biosynthesis of phosphorylated starch in intact potato amyloplasts
Abstract
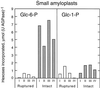
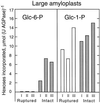
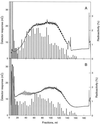
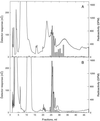
Intact amyloplasts from potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) were used to study starch biosynthesis and phosphorylation. Assessed by the degree of intactness and by the level of cytosolic and vacuolar contamination, the best preparations were selected by searching for amyloplasts containing small starch grains. The isolated, small amyloplasts were 80% intact and were free from cytosolic and vacuolar contamination. Biosynthetic studies of the amyloplasts showed that [1-14C]glucose-6-phosphate (Glc-6-P) was an efficient precursor for starch synthesis in a manner highly dependent on amyloplast integrity. Starch biosynthesis from [1-14C]Glc-1-P in small, intact amyloplasts was 5-fold lower and largely independent of amyloplast intactness. When [33P]Glc-6-P was administered to the amyloplasts, radiophosphorylated starch was produced. Isoamylase treatment of the starch followed by high-performance anion-exchange chromatography with pulsed amperometric detection revealed the separated phosphorylated alpha-glucans. Acid hydrolysis of the phosphorylated alpha-glucans and high-performance anion-exchange chromatography analyses showed that the incorporated phosphate was preferentially positioned at C-6 of the Glc moiety. The incorporation of radiolabel from Glc-1-P into starch in preparations of amyloplasts containing large grains was independent of intactness and most likely catalyzed by starch phosphorylase bound to naked starch grains.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Direct transport of ADPglucose by an adenylate translocator is linked to starch biosynthesis in amyloplasts.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5769-73. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5769. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991. PMID: 11607196 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylated alpha(1-->4)Glucans as substrate for potato starch-branching enzyme I.Plant Physiol. 1998 Jul;117(3):869-75. doi: 10.1104/pp.117.3.869. Plant Physiol. 1998. PMID: 9662529 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of temperature on starch synthesis in potato tuber tissue and in amyloplasts.Plant Physiol. 1988 Dec;88(4):1222-8. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.4.1222. Plant Physiol. 1988. PMID: 16666448 Free PMC article.
-
ADP-glucose drives starch synthesis in isolated maize endosperm amyloplasts: characterization of starch synthesis and transport properties across the amyloplast envelope.Biochem J. 1997 Jun 1;324 ( Pt 2)(Pt 2):503-9. doi: 10.1042/bj3240503. Biochem J. 1997. PMID: 9182710 Free PMC article.
-
[Starch metabolism in potato tubers].Postepy Biochem. 2009;55(4):441-6. Postepy Biochem. 2009. PMID: 20201358 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Functional characterization of alpha-glucan,water dikinase, the starch phosphorylating enzyme.Biochem J. 2004 Jan 15;377(Pt 2):525-32. doi: 10.1042/BJ20030999. Biochem J. 2004. PMID: 14525539 Free PMC article.
-
Plastids of three Cuscuta species differing in plastid coding capacity have a common parasite-specific RNA composition.Planta. 2003 Nov;218(1):135-42. doi: 10.1007/s00425-003-1082-8. Epub 2003 Jul 24. Planta. 2003. PMID: 12898255
-
Alpha-glucan, water dikinase (GWD): a plastidic enzyme with redox-regulated and coordinated catalytic activity and binding affinity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Feb 1;102(5):1785-90. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0406674102. Epub 2005 Jan 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15665090 Free PMC article.
-
Functional domain organization of the potato alpha-glucan, water dikinase (GWD): evidence for separate site catalysis as revealed by limited proteolysis and deletion mutants.Biochem J. 2005 Jan 15;385(Pt 2):355-61. doi: 10.1042/BJ20041119. Biochem J. 2005. PMID: 15361065 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-Glucan, Water Dikinase 1 Affects Starch Metabolism and Storage Root Growth in Cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz).Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 29;7(1):9863. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-10594-6. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28852191 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abel GJW, Springer F, Willmitzer L, Kossmann J. Cloning and functional analysis of a cDNA encoding a novel 139 kDa starch synthase from potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) Plant J. 1996;10:981–991. - PubMed
-
- Bay-Smidt AM, Wischmann B, Olsen CE, Nielsen TH. Starch bound phosphate in potato as studied by a simple method for determination of organic phosphate and 31P-NMR. Starch Stärke. 1994;46:167–172.
-
- Blennow A, Bay-Smidt AM, Wischmann B, Olsen CE, Møller BL. The degree of starch phosphorylation is related to the chain length distribution of the neutral and the phosphorylated chains of amylopectin. Carbohydr Res. 1998;307:45–54.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

