Purification and characterization of a NADPH-dependent aldehyde reductase from mung bean that detoxifies eutypine, a toxin from eutypa lata1
- PMID: 9952458
- PMCID: PMC32139
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.119.2.621
Purification and characterization of a NADPH-dependent aldehyde reductase from mung bean that detoxifies eutypine, a toxin from eutypa lata1
Abstract
Eutypine (4-hydroxy-3-[3-methyl-3-butene-1-ynyl] benzaldehyde) is a toxin produced by Eutypa lata, the causal agent of eutypa dieback in the grapevine (Vitis vinifera). Eutypine is enzymatically converted by numerous plant tissues into eutypinol (4-hydroxy-3-[3-methyl-3-butene-1-ynyl] benzyl alcohol), a metabolite that is nontoxic to grapevine. We report a four-step procedure for the purification to apparent electrophoretic homogeneity of a eutypine-reducing enzyme (ERE) from etiolated mung bean (Vigna radiata) hypocotyls. The purified protein is a monomer of 36 kD, uses NADPH as a cofactor, and exhibits a Km value of 6.3 &mgr;M for eutypine and a high affinity for 3- and 4-nitro-benzaldehyde. The enzyme failed to catalyze the reverse reaction using eutypinol as a substrate. ERE detoxifies eutypine efficiently over a pH range from 6.2 to 7.5. These data strongly suggest that ERE is an aldehyde reductase that could probably be classified into the aldo-keto reductase superfamily. We discuss the possible role of this enzyme in eutypine detoxification.
Figures
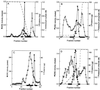

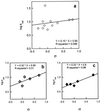
References
-
- Anzaï H, Yoneyama K, Yamaguchi I. Transgenic tobacco resistant to a bacterial disease by detoxification of a pathogenic toxin. Mol Gen Genet. 1989;219:492–494.
-
- Bohren KM, Bullock B, Wermuth B, Gabbay KH. The aldo-keto reductase superfamily. J Biol Chem. 1989;264:9547–9551. - PubMed
-
- Bohren KM, Page JL, Shankar R, Henry SP, Gabbay KH. Expression of human aldose and aldehyde reductases. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:24031–24037. - PubMed
-
- Colrat S, Deswarte C, Latché A, Klaébé A, Bouzayen M, Fallot J, Roustan JP (1998) Enzymatic detoxification of eutypine, a toxin from Eutypa lata, by Vitis vinifera cells: partial purification of an NADPH-dependent aldehyde reductase. Planta (in press)
-
- Damerval C, LeGuilloux M, Blaisonneau J, DeVienne D. A simplification of Heukeneneshoven and Dermick's silver staining of proteins. Electrophoresis. 1987;8:158–159.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

