The IS6110 restriction fragment length polymorphism in particular multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains may evolve too fast for reliable use in outbreak investigation
- PMID: 9986855
- PMCID: PMC84556
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.37.3.788-791.1999
The IS6110 restriction fragment length polymorphism in particular multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains may evolve too fast for reliable use in outbreak investigation
Abstract
To study possible nosocomial transmission of multidrug-resistant (MDR) Mycobacterium tuberculosis, strain types and other information on 24, mostly human immunodeficiency virus-positive patients, were collected. Isolates from 11 patients had identical IS6110 restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) patterns as well as spoligotype patterns and resistance profiles. Noticeably, nine other isolates from related cases also exhibited identical spoligotypes but slightly different RFLP patterns. These results indicate that for some MDR strains, the evolutionary clock of IS6110 RFLP may run too fast for reliable interpretation of strain typing results over a period of a few years.
Figures
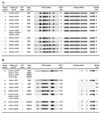

References
-
- Bifani P J, Plikaytis B B, Kapur V, Stockbauer K, Pan X, Lutfey M L, Moghazeh S L, Eisner W, Daniel T M, Kaplan M H, Crawford J T, Musser J M, Kreiswirth B N. Origin and interstate spread of a New York City multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis clone family. JAMA. 1996;275:452–457. - PubMed
-
- Canetti G, Rist N, Grosset J. Mesure de la sensibilite du bacille tuberculeux aux drogues antibacillaires pour la methode des proportions. Tubercle. 1963;27:217–272.
-
- Centro Panamericano de Zoonosis (CEPANZO, PAHO/WHO) Tuberculosis bacteriology. Technical note 11. Buenos Aires, Argentina: Centro Panamericano de Zoonosis; 1988. . (In Spanish.)
-
- Daley C L, Small P M, Schecter G F, Schoolnik G K, McAdam R A, Jacobs W R, Jr, Hopewell P C. An outbreak of tuberculosis with accelerated progression among persons infected with the human immunodeficiency virus. N Engl J Med. 1992;326:231–235. - PubMed
-
- Diaz R, Kremer K, de Haas P W E, Gomez R I, Marrero A, Valdivia J A, van Embden J D A, van Soolingen D. Molecular epidemiology of tuberculosis in Cuba, 1994–1995; comparison of IS6110 RFLP- and spoligotyping. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 1998;2:743–750. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

