Augmentation of antigen receptor-mediated responses by histamine H1 receptor signaling
- PMID: 9989982
- PMCID: PMC2192933
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.189.4.673
Augmentation of antigen receptor-mediated responses by histamine H1 receptor signaling
Abstract
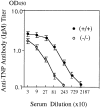
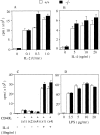
Histamine is considered one of the important mediators of immediate hypersensitivity and inflammation, and acts via G protein-coupled receptors. Here, we report that histamine may affect antigen receptor-mediated immune responses of T and B cells via a signal(s) from histamine H1 receptors (H1Rs). Histamine exhibited enhancing effects on the in vitro proliferative responses of anti-CD3epsilon- or anti-IgM-stimulated spleen T and B cells, respectively, at the culture condition that the fetal calf serum was dialyzed before culture and c-kit-positive cells were depleted from the spleen cells. In studies of histamine H1R knockout mice, H1R-deficient T cells had low proliferative responses to anti-CD3epsilon cross-linking or antigen stimulation in vitro. B cells from H1R-deficient mice were also affected, demonstrating low proliferative responses to B cell receptor cross-linking. Antibody production against trinitrophenyl-Ficoll was reduced in H1R-deficient mice. Other aspects of T and B cell function were normal in the H1R knockout mice. H1R-deficient T and B cells showed normal responses upon stimulation with interleukin (IL)-2, IL-4, CD40 ligand, CD40 ligand plus IL-4, and lipopolysaccharide. Collectively, these results imply that the signal generated by histamine through H1R augments antigen receptor-mediated immune responses, suggesting cross-talk between G protein-coupled receptors and antigen receptor-mediated signaling.
Figures
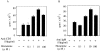






References
-
- Neer EJ. Heterotrimeric G proteins: organizers of transmembrane signaling. Cell. 1995;80:249–257. - PubMed
-
- Hamm HE, Gilchrist A. Heterotrimeric G proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996;8:189–196. - PubMed
-
- Kehrl HJ. Heterotrimeric G protein signaling: roles in immune function and fine-tuning by RGS protein. Immunity. 1998;8:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Post GR, Brown JH. G-protein-coupled receptors and signaling pathways regulating growth responses. FASEB (Fed Am Soc Exp Biol) J. 1996;10:741–749. - PubMed
-
- Wan Y, Kurosaki T, Huang XY. Tyrosine kinase in activation of the MAP kinase cascade by G-protein coupled receptors. Nature. 1996;380:541–544. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

