Femtosecond dynamics of the DNA intercalator ethidium and electron transfer with mononucleotides in water
- PMID: 9989999
- PMCID: PMC15438
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.4.1187
Femtosecond dynamics of the DNA intercalator ethidium and electron transfer with mononucleotides in water
Abstract
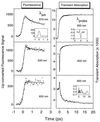
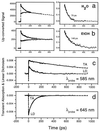
Ethidium (E) is a powerful probe of DNA dynamics and DNA-mediated electron transfer (ET). Molecular dynamical processes, such as solvation and orientation, are important on the time scale of ET. Here, we report studies of the femtosecond and picosecond time-resolved dynamics of E, E with 2'deoxyguanosine triphosphate (GTP) in water, and E with 7-deaza-2'-deoxyguanosine triphosphate (ZTP) in water; E undergoes ET with ZTP but not GTP. These studies elucidate the critical role of relative orientational motions of the donor-acceptor complex on ET processes in solution. For ET from ZTP to E, such motions are in fact the rate-determining step. Our results indicate that these complexes reorient before ET. The time scale for the solvation of E in water is 1 ps, and the orientational relaxation time of E is 70 ps. The impact of orientational and solvation effects on ET between E and mononucleotides must be considered in the application of E as a probe of DNA ET.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Simultaneous binding of minor groove binder and intercalator to dodecamer DNA: importance of relative orientation of donor and acceptor in FRET.J Phys Chem B. 2007 May 17;111(19):5047-52. doi: 10.1021/jp0715427. Epub 2007 Apr 25. J Phys Chem B. 2007. PMID: 17455977
-
Femtosecond dynamics of DNA-mediated electron transfer.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 May 25;96(11):6014-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.11.6014. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 10339533 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of ligands on the fluorescence polarisation anisotropy of ethidium bound to DNA.Biophys Chem. 1995 Feb;53(3):227-39. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(94)00099-6. Biophys Chem. 1995. PMID: 7533547
-
Synthesis and photophysical properties of zinc myoglobin appending an ethidium ion as a DNA intercalator.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2008 Feb;13(2):171-81. doi: 10.1007/s00775-007-0309-8. Epub 2007 Oct 18. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2008. PMID: 17943328
-
Ultrafast dynamics-driven biomolecular recognition where fast activities dictate slow events.J Biosci. 2018 Jul;43(3):485-498. J Biosci. 2018. PMID: 30002268 Review.
Cited by
-
The initial step of DNA hairpin folding: a kinetic analysis using fluorescence correlation spectroscopy.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 May 10;34(9):2516-27. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl221. Print 2006. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16687657 Free PMC article.
-
Base pair motions control the rates and distance dependencies of reductive and oxidative DNA charge transfer.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jul 5;103(27):10192-10195. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0600957103. Epub 2006 Jun 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16801552 Free PMC article.
-
Femtosecond direct observation of charge transfer between bases in DNA.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Dec 19;97(26):14052-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.250483297. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 11106376 Free PMC article.
-
Excess electron trapping in duplex DNA: long range transfer via stacked adenines.J Phys Chem B. 2012 Nov 8;116(44):13211-8. doi: 10.1021/jp307851g. Epub 2012 Oct 24. J Phys Chem B. 2012. PMID: 23067129 Free PMC article.
-
Femtosecond dynamics of flavoproteins: charge separation and recombination in riboflavine (vitamin B2)-binding protein and in glucose oxidase enzyme.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Oct 9;98(21):11867-72. doi: 10.1073/pnas.211440398. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11592997 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Le Pecq J-B, Paoletti C. J Mol Biol. 1967;27:87–106. - PubMed
-
- Burns V W F. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969;133:420–424. - PubMed
-
- Douthart R J, Burnett F W, Beasley F W, Frank B H. Biochemistry. 1973;12:214–220. - PubMed
-
- Bresloff J L, Crothers D M. J Mol Biol. 1975;95:103–123. - PubMed
-
- Waring M J. J Mol Biol. 1965;13:269–282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

