Acinar-to-Ductal Metaplasia Induced by Transforming Growth Factor Beta Facilitates KRASG12D-driven Pancreatic Tumorigenesis
- PMID: 28752115
- PMCID: PMC5524227
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2017.05.005
Acinar-to-Ductal Metaplasia Induced by Transforming Growth Factor Beta Facilitates KRASG12D-driven Pancreatic Tumorigenesis
Abstract
Background & aims: Transforming growth factor beta (TGFβ) acts either as a tumor suppressor or as an oncogene, depending on the cellular context and time of activation. TGFβ activates the canonical SMAD pathway through its interaction with the serine/threonine kinase type I and II heterotetrameric receptors. Previous studies investigating TGFβ-mediated signaling in the pancreas relied either on loss-of-function approaches or on ligand overexpression, and its effects on acinar cells have so far remained elusive.
Methods: We developed a transgenic mouse model allowing tamoxifen-inducible and Cre-mediated conditional activation of a constitutively active type I TGFβ receptor (TβRICA) in the pancreatic acinar compartment.
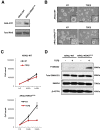
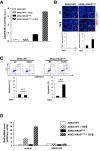
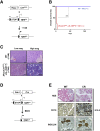
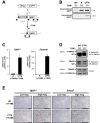
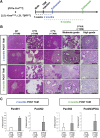
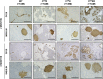
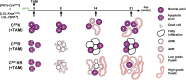
Results: We observed that TβRICA expression induced acinar-to-ductal metaplasia (ADM) reprogramming, eventually facilitating the onset of KRASG12D-induced pre-cancerous pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia. This phenotype was characterized by the cellular activation of apoptosis and dedifferentiation, two hallmarks of ADM, whereas at the molecular level, we evidenced a modulation in the expression of transcription factors such as Hnf1β, Sox9, and Hes1.
Conclusions: We demonstrate that TGFβ pathway activation plays a crucial role in pancreatic tumor initiation through its capacity to induce ADM, providing a favorable environment for KRASG12D-dependent carcinogenesis. Such findings are highly relevant for the development of early detection markers and of potentially novel treatments for pancreatic cancer patients.
Keywords: ADM, acinar-to-ductal metaplasia; AFI, acinar fatty infiltration; Acinar-to-Ductal Metaplasia; Cancer; EMT, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition; KRASG12D; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; PDA, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; PanIN, pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia; Pancreas; RT-qPCR, reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction; TGFβ; TGFβ, transforming growth factor beta; TUNEL, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling.
Figures





References
-
- Jorgensen M.C., Ahnfelt-Ronne J., Hald J., Madsen O.D., Serup P., Hecksher-Sorensen J. An illustrated review of early pancreas development in the mouse. Endocr Rev. 2007;28:685–705. - PubMed
-
- Shih H.P., Wang A., Sander M. Pancreas organogenesis: from lineage determination to morphogenesis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2013;29:81–105. - PubMed
-
- Pan F.C., Wright C. Pancreas organogenesis: from bud to plexus to gland. Dev Dyn. 2011;240:530–565. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

