Ex Vivo Live Full-Thickness Porcine Skin Model as a Versatile In Vitro Testing Method for Skin Barrier Research
- PMID: 33440780
- PMCID: PMC7827261
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22020657
Ex Vivo Live Full-Thickness Porcine Skin Model as a Versatile In Vitro Testing Method for Skin Barrier Research
Abstract
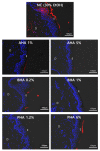
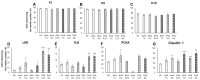
Since the European Union (EU) announced their animal testing ban in 2013, all animal experiments related to cosmetics have been prohibited, creating a demand for alternatives to animal experiments for skin studies. Here, we investigated whether an ex vivo live porcine skin model can be employed to study the safety and skin barrier-improving effects of hydroxyacids widely used in cosmetics for keratolytic peels. Glycolic acid (1-10%), salicylic acid (0.2-2%), and lactobionic acid (1.2-12%) were used as representative substances for α-hydroxyacid (AHA), β-hydroxyacid (BHA), and polyhydroxyacid (PHA), respectively. When hydroxyacids were applied at high concentrations on the porcine skin every other day for 6 days, tissue viability was reduced to 50-80%, suggesting that the toxicity of cosmetic ingredients can be evaluated with this model. Based on tissue viability, the treatment scheme was changed to a single exposure for 20 min. The protective effects of a single exposure of hydroxyacids on skin barrier function were evaluated by examining rhodamine permeability and epidermal structural components of barrier function using immunohistochemistry (IHC) and immunofluorescence (IF) staining. Lactobionic acid (PHAs) improved skin barrier function most compared to other AHAs and BHAs. Most importantly, trans-epidermal water loss (TEWL), an important functional marker of skin barrier function, could be measured with this model, which confirmed the significant skin barrier-protective effects of PHAs. Collectively, we demonstrated that the ex vivo live full-thickness porcine skin model can be an excellent alternative to animal experiments for skin studies on the safety and efficacy of cosmetic ingredients.
Keywords: ex vivo skin model; hydroxyacids; skin barrier; skin permeability; stratum corneum.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Forslind B. A domain mosaic model of the skin barrier. Acta Dermato-Venereol. 1994;74:1–6. - PubMed
-
- Choi J.H., Jin S.W., Lee G.H., Cho S.M., Jeong H.G. Orostachys japonicus ethanol extract inhibits 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice and TNF-alpha/IFN-gamma-induced TARC expression in HaCaT cells. Toxicol. Res. 2020;36:99–108. doi: 10.1007/s43188-019-00026-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barel A.O., Paye M., Maibach H.I. Handbook of Cosmetic Science and Technology. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2014.
-
- Duracher L., Visdal-Johnsen L., Mavon A., Oriflame Cosmetics A.B. Novel Explant Model for Skin Delivery Assessment. Cosm. Toil. 2015;130:30–40.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

