Neddylation regulation of mitochondrial structure and functions
- PMID: 33731189
- PMCID: PMC7968265
- DOI: 10.1186/s13578-021-00569-6
Neddylation regulation of mitochondrial structure and functions
Abstract
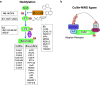
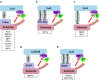
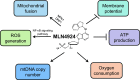
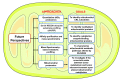
Mitochondria are the powerhouse of a cell. The structure and function of mitochondria are precisely regulated by multiple signaling pathways. Neddylation, a post-translational modification, plays a crucial role in various cellular processes including cellular metabolism via modulating the activity, function and subcellular localization of its substrates. Recently, accumulated data demonstrated that neddylation is involved in regulation of morphology, trafficking and function of mitochondria. Mechanistic elucidation of how mitochondria is modulated by neddylation would further our understanding of mitochondrial regulation to a new level. In this review, we first briefly introduce mitochondria, then neddylation cascade, and known protein substrates subjected to neddylation modification. Next, we summarize current available data of how neddylation enzymes, its substrates (including cullins/Cullin-RING E3 ligases and non-cullins) and its inhibitor MLN4924 regulate the structure and function of mitochondria. Finally, we propose the future perspectives on this emerging and exciting field of mitochondrial research.
Keywords: Cullin-RING ligases; Energy metabolism; MLN4924; Mitochondria; Neddylation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Li S, Pan H, Tan C, Sun Y, Song Y, Zhang X, Yang W, Wang X, Li D, Dai Y, Ma Q, Xu C, Zhu X, Kang L, Fu Y, Xu X, Shu J, Zhou N, Han F, Qin D, Huang W, Liu Z, Yan Q. Mitochondrial dysfunctions contribute to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in patient iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes with MT-RNR2 mutation. Stem cell Rep. 2018;10(3):808–821. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2018.01.013. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

