scCompass: An Integrated Multi-Species scRNA-seq Database for AI-Ready
- PMID: 40317650
- PMCID: PMC12224968
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202500870
scCompass: An Integrated Multi-Species scRNA-seq Database for AI-Ready
Abstract
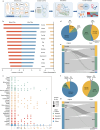
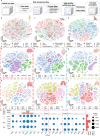
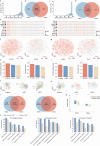
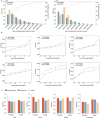
Emerging single-cell sequencing technology has generated large amounts of data, allowing analysis of cellular dynamics and gene regulation at the single-cell resolution. Advances in artificial intelligence enhance life sciences research by delivering critical insights and optimizing data analysis processes. However, inconsistent data processing quality and standards remain to be a major challenge. Here scCompass is proposed, which provides a comprehensive resource designed to build large-scale, multi-species, and model-friendly single-cell data collection. By applying standardized data pre-processing, scCompass integrates and curates transcriptomic data from nearly 105 million single cells across 13 species. Using this extensive dataset, it is able to identify stable expression genes (SEGs) and organ-specific expression genes (OSGs) in humans and mice. Different scalable datasets are provided that can be easily adapted for AI model training and the pretrained checkpoints with state-of-the-art single-cell foundation models. In summary, scCompass is highly efficient and scalable database for AI-ready, which combined with user-friendly data sharing, visualization, and online analysis, greatly simplifies data access and exploitation for researchers in single-cell biology (http://www.bdbe.cn/kun).
Keywords: AI‐ready; multi‐species; scRNA‐seq database; single‐cell.
© 2025 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Sun F., Li H., Sun D., Fu S., Gu L., Shao X., Wang Q., Dong X., Duan B., Xing F., Wu J., Xiao M., Zhao F., Han J. J., Liu Q., Fan X., Li C., Wang C., Shi T., Science China Life Sciences 2024, 1, 68. - PubMed
-
- Beumer J., Clevers H., Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 39. - PubMed
-
- Qiu C., Martin B. K., Welsh I. C., Daza R. M., Le T.‐M., Huang X., Nichols E. K., Taylor M. L., Fulton O., O'Day D. R., Gomes A. R., Ilcisin S., Srivatsan S., Deng X., Disteche C. M., Noble W. S., Hamazaki N., Moens C. B., Kimelman D., Cao J., Schier A. F., Spielmann M., Murray S. A., Trapnell C., Shendure J., Nature 2024, 626, 1084. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 92470204/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2024YFF0729201/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2024YFF0729200/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- XDA0460305toG.F./Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences
- YSBR-076/CAS Project for Young Scientists in Basic Research
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
