SARS-CoV-2 pandemic and research gaps: Understanding SARS-CoV-2 interaction with the ACE2 receptor and implications for therapy
- PMID: 32642005
- PMCID: PMC7330865
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.48076
SARS-CoV-2 pandemic and research gaps: Understanding SARS-CoV-2 interaction with the ACE2 receptor and implications for therapy
Abstract
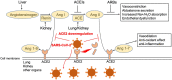
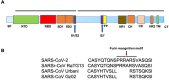
The COVID-19 pandemic is an emerging threat to global public health. While our current understanding of COVID-19 pathogenesis is limited, a better understanding will help us develop efficacious treatment and prevention strategies for COVID-19. One potential therapeutic target is angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). ACE2 primarily catalyzes the conversion of angiotensin I (Ang I) to a nonapeptide angiotensin or the conversion of angiotensin II (Ang II) to angiotensin 1-7 (Ang 1-7) and has direct effects on cardiac function and multiple organs via counter-regulation of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS). Significant to COVID-19, ACE2 is postulated to serve as a major entry receptor for SARS-CoV-2 in human cells, as it does for SARS-CoV. Many infected individuals develop COVID-19 with fever, cough, and shortness of breath that can progress to pneumonia. Disease progression promotes the activation of immune cells, platelets, and coagulation pathways that can lead to multiple organ failure and death. ACE2 is expressed by epithelial cells of the lungs at high level, a major target of the disease, as seen in post-mortem lung tissue of patients who died with COVID-19, which reveals diffuse alveolar damage with cellular fibromyxoid exudates bilaterally. Comparatively, ACE2 is expressed at low level by vascular endothelial cells of the heart and kidney but may also be targeted by the virus in severe COVID-19 cases. Interestingly, SARS-CoV-2 infection downregulates ACE2 expression, which may also play a critical pathogenic role in COVID-19. Importantly, targeting ACE2/Ang 1-7 axis and blocking ACE2 interaction with the S protein of SARS-CoV-2 to curtail SARS-CoV-2 infection are becoming very attractive therapeutics potential for treatment and prevention of COVID-19. Here, we will discuss the following subtopics: 1) ACE2 as a receptor of SARS-CoV-2; 2) clinical and pathological features of COVID-19; 3) role of ACE2 in the infection and pathogenesis of SARS; 4) potential pathogenic role of ACE2 in COVID-19; 5) animal models for pathological studies and therapeutics; and 6) therapeutics development for COVID-19.
Keywords: ACE2; COVID-19; and animal model; pathogenesis; spike protein.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Organ-protective effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and its effect on the prognosis of COVID-19.J Med Virol. 2020 Jul;92(7):726-730. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25785. Epub 2020 Apr 5. J Med Virol. 2020. PMID: 32221983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), SARS-CoV-2 and the pathophysiology of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).J Pathol. 2020 Jul;251(3):228-248. doi: 10.1002/path.5471. Epub 2020 Jun 10. J Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32418199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A brief review of interplay between vitamin D and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: Implications for a potential treatment for COVID-19.Rev Med Virol. 2020 Sep;30(5):e2119. doi: 10.1002/rmv.2119. Epub 2020 Jun 25. Rev Med Virol. 2020. PMID: 32584474 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The mechanistic overview of SARS-CoV-2 using angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 to enter the cell for replication: possible treatment options related to the renin-angiotensin system.Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother. 2020 Sep 1;6(5):317-325. doi: 10.1093/ehjcvp/pvaa053. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32464637 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor and SARS-CoV-2: Potential therapeutic targeting.Eur J Pharmacol. 2020 Oct 5;884:173455. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173455. Epub 2020 Jul 31. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32745604 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiovascular Comorbidities in COVID-19: Comprehensive Analysis of Key Topics.Interact J Med Res. 2024 Jul 24;13:e55699. doi: 10.2196/55699. Interact J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39046774 Free PMC article.
-
Spike-based adenovirus vectored COVID-19 vaccine does not aggravate heart damage after ischemic injury in mice.Commun Biol. 2022 Sep 2;5(1):902. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03875-y. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 36056135 Free PMC article.
-
Direct, indirect, post-infection damages induced by coronavirus in the human body: an overview.Virusdisease. 2022 Dec;33(4):429-444. doi: 10.1007/s13337-022-00793-9. Epub 2022 Oct 25. Virusdisease. 2022. PMID: 36311173 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Interplay among Glucocorticoid Therapy, Platelet-Activating Factor and Endocannabinoid Release Influences the Inflammatory Response to COVID-19.Viruses. 2023 Feb 19;15(2):573. doi: 10.3390/v15020573. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36851787 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular Immunity Is Critical for Assessing COVID-19 Vaccine Effectiveness in Immunocompromised Individuals.Front Immunol. 2022 May 26;13:880784. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.880784. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35693815 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harmer D, Gilbert M, Borman R, Clark KL. Quantitative mRNA expression profiling of ACE 2, a novel homologue of angiotensin converting enzyme. FEBS letters. 2002;532:107–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

