TCR-T Cell Recognition of an NY-ESO-1 Epitope Presented by HLA-A2 Supertype: Implications for Cancer Immunotherapy
- PMID: 41012104
- PMCID: PMC12474311
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines13090898
TCR-T Cell Recognition of an NY-ESO-1 Epitope Presented by HLA-A2 Supertype: Implications for Cancer Immunotherapy
Abstract
Background: T-cell receptor (TCR)-engineered T-cell therapy (TCR-T) has become a promising anticancer therapy. Recognition of tumor cells by TCR-T cells requires matched human leukocyte antigen (HLA) alleles and tumor antigens, which seriously limits their population coverage. One strategy to expand the population coverage of a specific TCR-T cell therapy is to enable TCR-T cells to recognize target peptides presented by more HLA alleles.
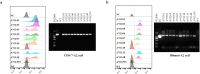
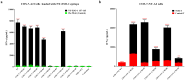
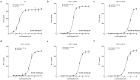
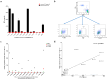
Methods: In this study, HLA alleles were selected based on the Chinese population frequency and HLA supertype classification. Then, COS-7 and two tumor cell lines (586 mel and 5637) were transduced with selected HLA alleles for functional evaluation of TCR-T cells. HLA-A2 alleles capable of both exogenously and endogenously presenting the NY-ESO-1-derived epitope and thereby being recognized by TCR-T cells were tested.
Results: We demonstrated that a given TCR-T cell product can recognize the NY-ESO-1 peptide exogenously and endogenously presented not only by HLA-A*02:01 but also by HLA-A*02:03, HLA-A*02:06, and HLA-A*02:10, almost doubling the population coverage in the Chinese population from 12.01% to 21.05%.
Conclusions: Our study suggests that cancer patients expressing members of the HLA-A2 supertype may benefit from the TCR-T cell product, and other TCR-T cell products could similarly expand their population coverage even within the non-Chinese population through an analogous approach.
Keywords: HLA-A2 alleles; HLA-A2 supertype; NY-ESO-1; TCR-T; cancer immunotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Qingqing Lin, Fenglan Liu, Yipeng Ma, Yanwei Li, Tong Lin, Xiaochun Chen, Jinling Zhang and Zhi Wang were employed by Shenzhen Innovation Immunotechnology Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Nagarsheth N.B., Norberg S.M., Sinkoe A.L., Adhikary S., Meyer T.J., Lack J.B., Warner A.C., Schweitzer C., Doran S.L., Korrapati S., et al. TCR-engineered T cells targeting E7 for patients with metastatic HPV-associated epithelial cancers. Nat. Med. 2021;27:419–425. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-01225-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- KJZD20240903102713018/Shenzhen Major Science and Technology Special Project
- JCYJ20180507182902330 and JCYJ20190809115811354/Shenzhen Basic Research Program
- KQTD20130416114522736/Shenzhen Peacock Plan
- KJYF202001-13, KJYF202001-12, KY20180214, PT201901-12/Special Funds for Dapeng New District Industry Development
- CJGJZD20200617102403009/Shenzhen Science and Technology Research and Development Fund
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

